In the forex economic calendar, there are significant data that traders should pay attention to for trading. One of these data is the gross domestic product (GDP). Gross domestic product is one of the main macroeconomic indicators in forex. It refers to the total amount spent on final goods & services and is calculated in different periods. The period is usually quarterly, i.e., once every three months. GDP is a standard measure of added value to the country’s economy through goods production and services in a specific period. GDP is published by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and you can find related information on their official website, and the Trendo economic calendar.
As explained earlier, GDP measures the health of an economy. If a country’s GDP is high, it indicates that the flow of capital leaves the central bank and financial institutions and goes toward the economy’s prosperity, which is a positive point for that country. However, if quarterly GDP numbers are declining, it means the country’s economic growth has slowed. In such a situation, unemployment in the country increases, and production efficiency decreases. GDP is important because it provides a broad view of the economy’s state and is a sign that there are more jobs, people are getting paid better, and businesses are more confident about investing.
How to Calculate GDP
The GDP of a country can be calculated using the following formula:
GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
C: Costs incurred by consumers
These costs include all purchases by individuals for personal use and include consumer goods such as food and clothing, durable goods such as cars and household appliances, and services provided such as mechanics or lawyers.
I: Invested amount by businesses
This amount describes the purchases made by a business unit and is divided into two categories: fixed assets and inventory. Fixed assets are anything a company buys, such as real estate, patents, machinery, and employee salaries. All fixed assets except land are depreciated. On the other hand, inventory is all the goods produced by a company that has not been sold and are still counted in the value of a business because they are considered to generate revenue eventually.
G: Government spending
Government spending in GDP is expenses that governments spend, such as paying workers, military spending, and infrastructure spending. These components of the government’s GDP are considered goods and services produced in the country, so their costs are included in the gross domestic product calculation.
(X-M): Net exports
Net exports include all goods and services produced domestically but sold to foreigners. The amount of net import is calculated by deducting import costs from export profits. Imports are not produced domestically, so the cost of these international goods and services is subtracted from a country’s GDP because the money paid is taken out of the economy.
Types of GDP: Nominal or Real
Nominal GDP is the sum of goods and services consumed plus government spending, investments, and exports, minus total imports, but the inflation or disinflation effects and currency fluctuations can give an inaccurate picture of how much an economy is growing or stagnating in any given period.
The amount of real GDP is adjusted upwards or downwards to reduce the effects of inflation or deflation and currency fluctuations. By removing the effect of inflation, real GDP is a more accurate reflection of an economy’s output than nominal GDP, giving a clearer idea of how the total national production of a country grows or decreases.
For example, consider a hypothetical country whose nominal GDP was $100 billion in 2010, while its nominal GDP was $150 billion in 2020. In the same period, inflation has reduced the relative value of that country’s money by 50%. Just by looking at the nominal GDP, it seems the economy has grown by 50% in 10 years. But real GDP adjusted for inflation will be $75 billion in 2020, which shows a significant decrease.
GDP growth rate
The GDP growth rate measures the percentage change in real GDP (GDP adjusted for inflation) from one period to another, usually as a comparison between the most recent quarter or year and the previous quarter. This index can be a positive or negative number (negative growth rate, indicating contractionary policies).
GDP per capita
GDP per capita is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP by a country’s total population, showing the average economic output (or income) per person.
How does GDP affect the Forex market?
GDP is a measure of a country’s economic performance and is a vital indicator of that country’s economic health. When the GDP is high, it indicates that the country produces more goods & services and people earn more. A high GDP is usually associated with a strong economy, and this can lead to a stronger currency.A country with a high GDP is more likely to attract foreign investment, which can increase the demand for its currency and increase its value.
When a country’s GDP is low, it indicates that the economy is not producing enough goods & services and people are not earning enough. In this case, the currency may weaken because foreign investors are less likely to invest in a country with a struggling economy. A low GDP can also lead to inflation, which can devalue a currency.
In addition to the overall GDP level, its growth rate is a fundamental factor in the forex market. If a country’s GDP grows faster than its trading partners, its currency’s value may increase against them. Because investors are more willing to invest in a country with a growing economy because they believe in the future, its currency will become more valuable. Conversely, if a country’s GDP growth rate is slower than its trading partners, its currency’s value may depreciate against them. That is because investors are less likely to invest in a country with slower economic growth. After all, they believe that in the future, its currency will be worth less.
It is important to note that the relationship between GDP and the forex market is not always straightforward. Several other factors can affect the value of a currency, including interest rates, political stability, and inflation. For example, even if a country has a high GDP, when its political situation is unstable, or inflation is high, its currency may still weaken. Therefore, GDP should be reviewed with a country’s monetary policy.
In addition, the impact of GDP on forex can vary depending on the country’s economic structure. For example, a predominantly export-oriented country may benefit from a weaker currency because it makes its goods and services more affordable to foreign buyers. Conversely, a largely import-oriented country may benefit from a stronger currency because it makes imported goods cheaper for its citizens.
Note that GDP is a lagged indicator, meaning it shows what the economy has done in the past and does not predict the future economy’s state. Also, at present, we can determine the general state of a country’s economy with data such as employment and inflation, etc., published monthly. Therefore, if the GDP data of a country is not good, it means that the past state of the country’s economy was not good, and the government will probably adopt supportive policies for the economy. As a result, traders see this as an opportunity to buy currency and earn long-term profits.
In general, if the GDP index is published in the economic calendar according to the forecasts, it cannot have a notable effect on a country’s currency. However, it can cause a good fluctuation in the desired currency in the short term if it surprises the market and publishes higher or lower than the predictions. Higher than expected causes the currency to become stronger, and lower than expected causes the currency to weaken.
How GDP affects currencies in the long run
High GDP affects currencies in the long run by increasing the demand for currency both domestically and internationally. Countries with high GDP are considered emerging markets because their economies grow in monetary terms. For example, if a country has a GDP of $3.53 trillion and maintains a 7% annual growth rate for a full year, its economy grows to $3.78 trillion. This growth is $247 billion. This growth also increases the demand for currency. You can remember this by recalling that a high GDP results from an increase in the production rate, which in turn means growth in demand for the country’s products. In this case, supply is based on demand. High demand for a country’s products also usually means high demand for the country’s currency to buy that country’s products. When the economic growth of a country, and with it the demand for its money, exceeds the economic growth of another country, the exchange rate value of two currencies changes.
An example of the GDP growth’s long-term effects in Forex
For an example of how GDP can be used in forex trading, let’s look at the long-term GDP growth rate between the Eurozone and the United States and the value of EUR/USD. The chart below shows the annual GDP of the United States and the European Union from 2004 to 2017.
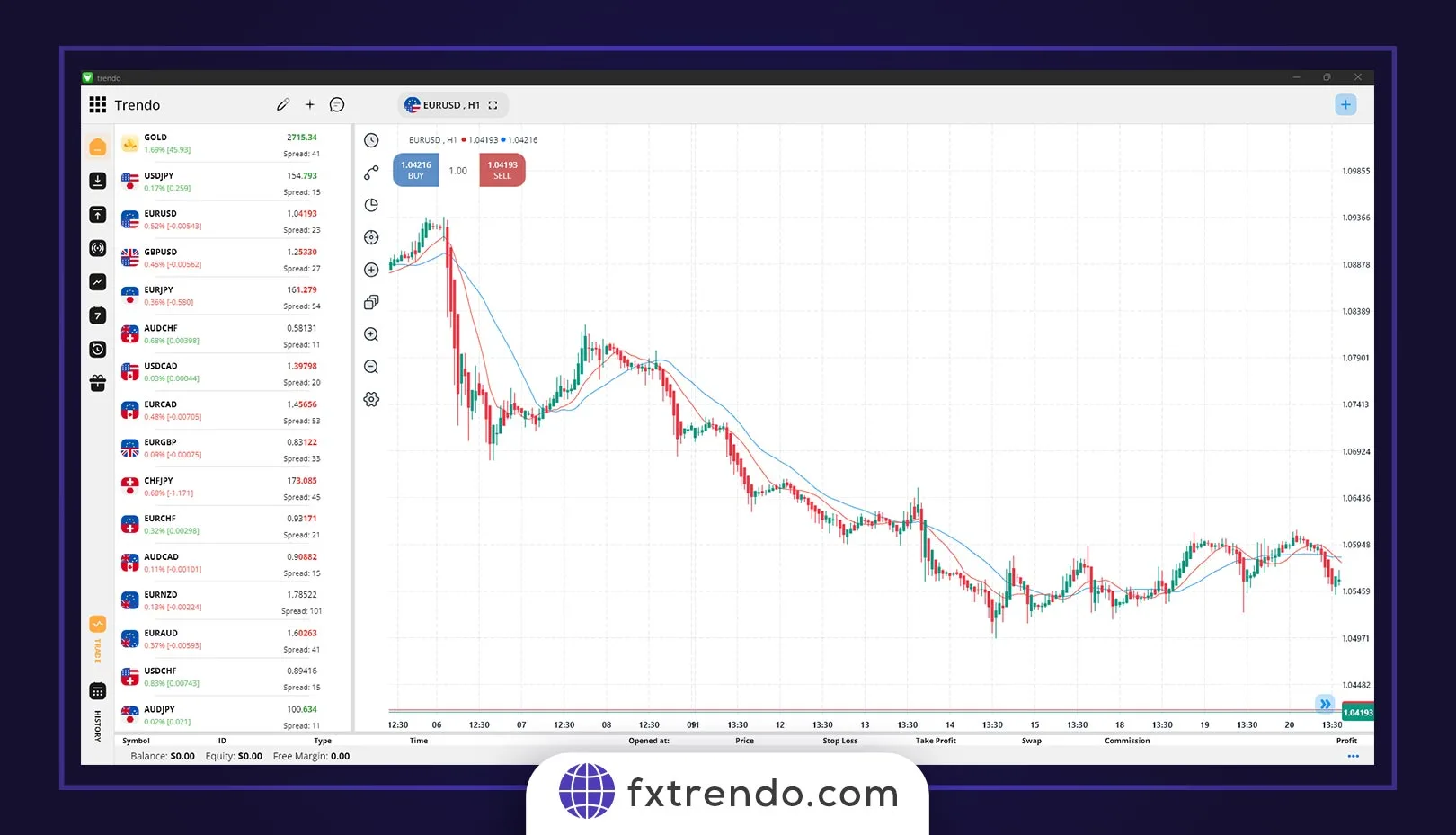
Immediately before the global financial crisis in 2008, the Eurozone outperformed the United States in terms of economic performance. Both economies went into recession in 2009 after the crisis. A recession is usually two consecutive periods of negative GDP growth. After the crisis, the US annual GDP rate was consistently higher than the Eurozone. That suggests that the Eurozone economy has been hit worse than the US and has taken longer to recover. From 2010 to 2011, subsequent economic problems, such as the Greek debt crisis shook Europe.
Now let’s compare the GDP growth rate shown above with the value of EUR/USD. Euro was steadily increasing against the dollar from mid-2005 to early 2008. Looking at the graph above, this corresponds to when the GDP rate of the Eurozone was higher than the United States.
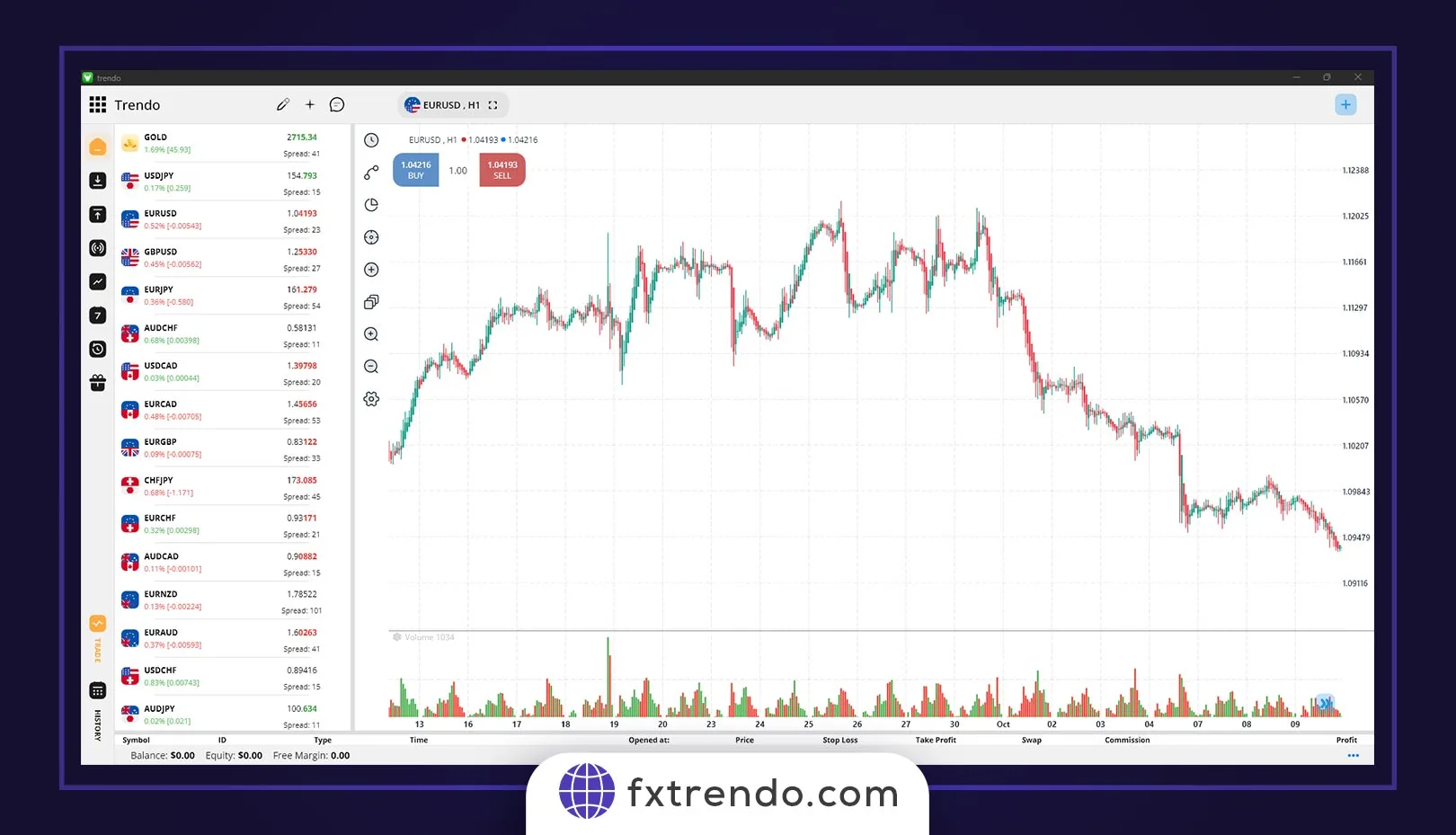
However, the financial crisis affected Europe as much as the United States over time. The dollar had already experienced a devaluation due to the crisis, so when Euro followed suit, it depreciated sharply and quickly against the dollar.
Then the dollar slowly recovered while the Greek debt crisis and other issues affected Europe. This divergence between the two economies caused the Euro to sell off in 2014 and devalued the Euro/USD.
How GDP affects currencies in the short term
GDP can quickly affect the value of currencies if the GDP report is significantly lower or higher than economists and traders expect.
How Less-than-expected GDP Affects The Forex Market
Less-than-expected GDP reports can cause volatility in related currency pairs, as a less-than-expected number means the economy isn’t growing as fast as predicted, or depending on how you look at it, it’s growing even slower than expected. This news may cause traders and investors to lose confidence and influence them to sell the currency in question due to the possibility of further decline.
For example, traders with a long EUR/USD position may sell the EUR and close their position when a less-than-expected GDP rate is reported for the EU. Some may even take short positions in EUR/USD.
How Higher-than-expected GDP Affects Forex
A higher-than-expected GDP report may boost a currency’s value in the forex market. If no other factor has a stronger influence on a currency, its value may increase relative to a currency with a lower GDP. A higher-than-expected value may indicate that the economy is growing faster than predicted, or doesn’t slow down suddenly. That can increase traders’ faith in the currency. However, if this rate is too high, it may cause fear of inflation and destroy trust in the currency. Therefore, higher GDP rates can be harder to decipher.
For example, if the UK GDP rate is reported at 3% when expected to be 2.5%, traders may take that as a sign that the pound is growing more than expected. If a counter-currency such as the US dollar does not rise at a similar rate, traders may open a long position in the GBP/USD currency pair. If the rate is reported at 4%, when 2.5% is expected, growth may be considered too strong. In response, traders may avoid opening long positions in the pound if they suspect rising inflation.
When does GDP affect the Forex market?
GDP reports may not affect Forex if the average rate is overshadowed by another economic event or canceled by inflation, as expected. GDP rates that match forecast numbers, especially in the 2-3% range, may not be newsworthy enough to affect trader sentiment. In addition, markets may be affected by stronger economic news, and in the end, inflation often offsets GDP growth.
Summary
GDP is a critical indicator of a country’s economic health, and changes in GDP can significantly impact the forex market. Strong GDP is usually associated with a strong currency, while weak GDP can lead to a weaker currency. However, the relationship between GDP and Forex is not always straightforward, and several other factors can affect a currency’s value. Investors and traders should consider a variety of economic indicators when deciding whether to invest in the forex market.