Pump and dump usually happen in financial markets such as forex and cryptocurrency, and are difficult to predict. A pump and dump pattern usually represents the disturbance created by major market players that directly affects the increase or decrease in the asset price. To find the answer to the “what does pump and dump mean?” question, read theis article carefully.
What is pump and dump?
The pump and dump definition is provided in this section. A Pump and Dump scheme is a form of price manipulation and we can define pump and dump like that. Big market players sometimes spread rumors about an asset’s price, which leads to misleading rookie traders and extreme price fluctuations. They buy the asset at a low price and then sell it at a very high price. When fraudsters buy stocks, currency pairs, or cryptocurrencies, they advertise a lot and create hype. After that, as investors and retail traders come in, players sell their assets to rookies at higher prices. As a result, traders lose a huge amount of their money due to the lack of liquidity and the sharp price drop due to selling pressure.
How does pump and dump occur?
Now that you understand the pump and dump meaning, that is the time to be familiar with pump and dump occuring. In a Pump and Dump scheme, operators claim to have deep fundamental knowledge of the project that backs up their claims about the potential for price increases. They usually use social media to spread their claims and often engage influencers or celebrities to promote the project to their followers. When the price jumps in response to the entry of buyers into the market, the scammers take their profits, and the large sell volume causes the price to suddenly fall.
Read More: Useful and important indicators for fundamental analysis in cryptocurrencies.
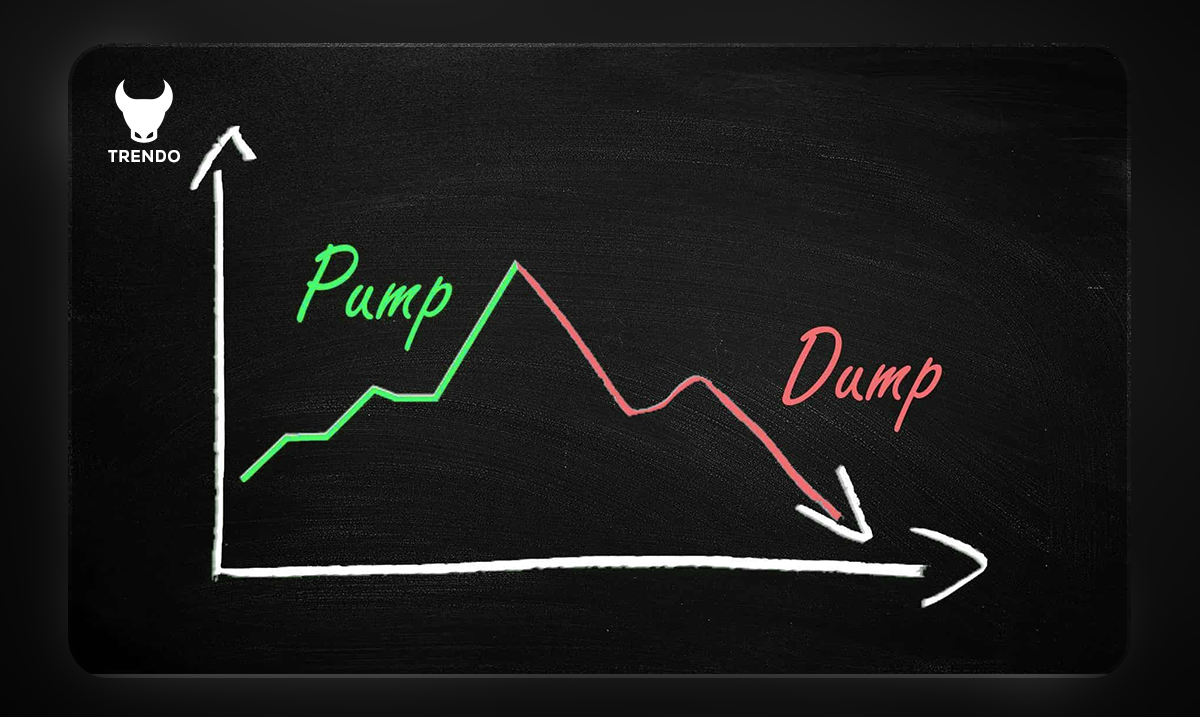
The Anatomy of a Pump and Dump
A pump and dump usually follows a repeatable pattern—knowing the sequence helps you spot it early.
Accumulation: A small group quietly builds a position over time, typically in a low-liquidity asset. You’ll often see “boring” price action with thin order books and occasional small spikes designed to test liquidity.
Promotion: Hype begins—Telegram/Discord channels, influencer posts, “leaked news,” or exaggerated catalysts. Watch for coordinated messaging, aggressive price targets, and urgency (“last chance,” “next 100x”).
Pump: Price accelerates fast, often with sudden volume expansion and wide spreads. Candles become unusually large, pullbacks get shallow, and late buyers chase breakouts. This phase is often fueled by market orders and FOMO, may lead to a market pump.
Dump: The group sells into the demand they created. You’ll see sharp wicks, failed breakouts, heavy sell volume, and a rapid drop. Liquidity vanishes, slippage increases, and attempts to “buy the dip” keep failing.
An example of Pump and Dump scheme in cryptocurrencies
Several Pump and Dump schemes have occurred in cryptocurrencies over the past few years. Unfortunately, these scams are directly related to one of the most basic human emotions, namely greed, and this has caused many people to lose their capital in this process.
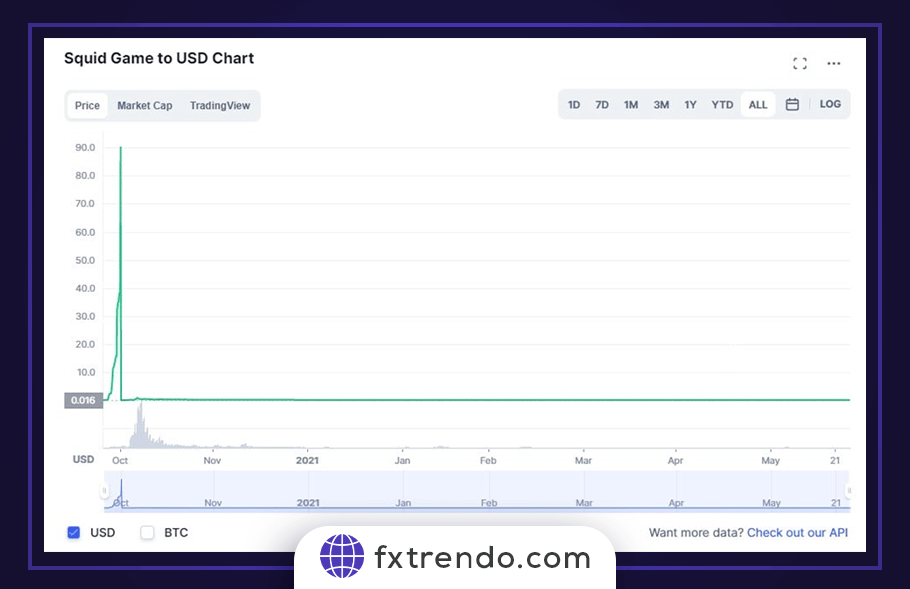
One of the strangest scams was in the form of Squid Game. It’s named after the hit Netflix movie Squid Game. The token had nothing to do with Netflix or the movie but people jumped in based on the hype, and its value went from $0.01 to nearly $2,800 before falling again moments later. Scammers of this project earned $2 million in just a few moments.
Pump and Dump in Cryptocurrencies vs Stocks
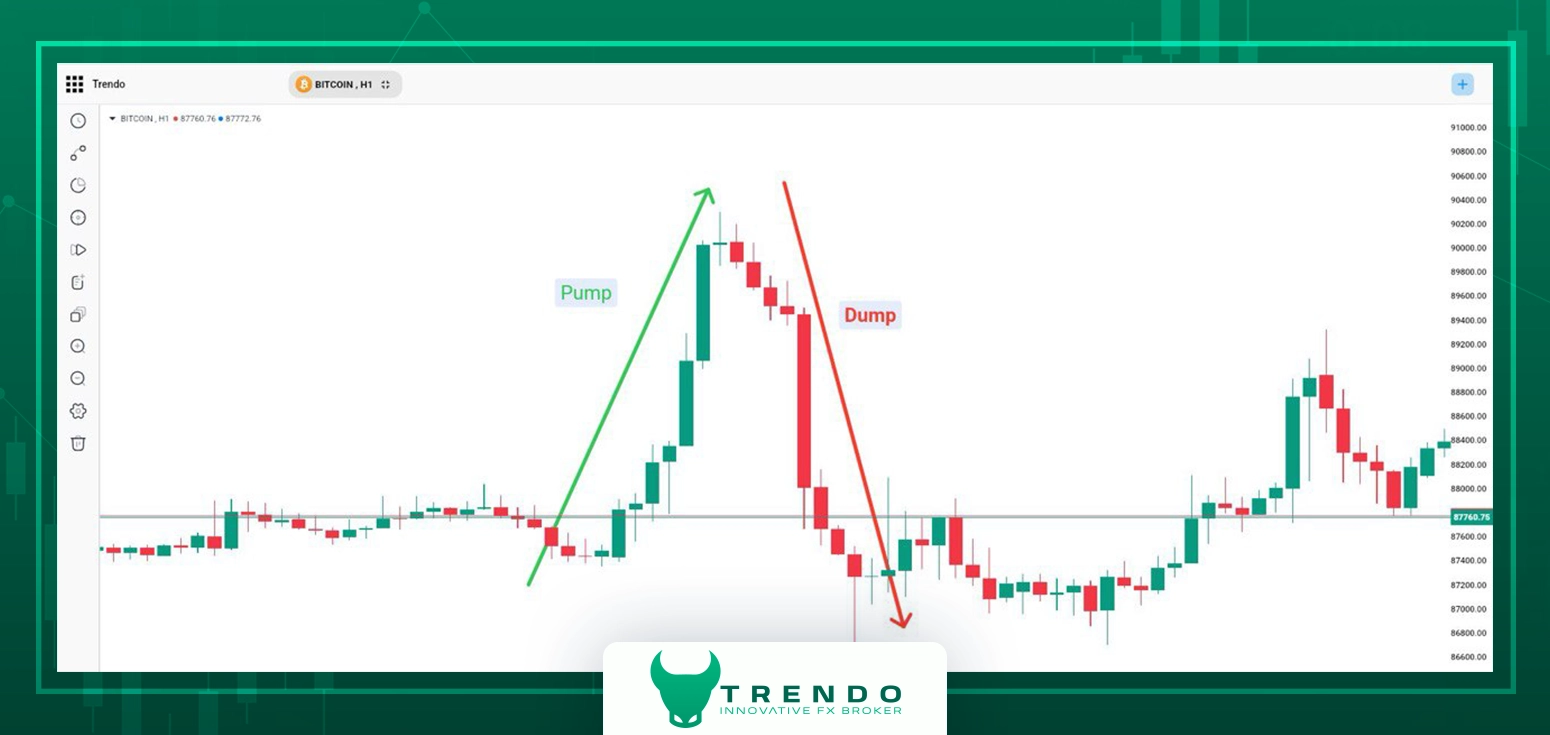
Cryptocurrencies are more vulnerable because many tokens have low liquidity, fragmented venues, and 24/7 trading. It is a decentralized marker which is further considered as a threat. Coordination is easier (social channels), and offshore exchanges may have weaker surveillance. Pumps can be faster and more extreme due to thin order books and high leverage availability. The following figure showas an example of pump and dump chart in crypto market.
Stocks can still be manipulated—especially microcaps—but regulated exchanges and disclosure rules create more friction. Promotion often uses newsletters, forums, or misleading press releases. Trading halts, broker restrictions, and enforcement actions are more common in equities, which can limit (but not eliminate) the damage.
In practice: crypto pumps tend to be more frequent and violent, while stock pumps are often more structured, catalyst-driven, and constrained by regulation—yet still dangerous in illiquid names.
How to distinguish pump and dump schemes?
The easiest way to recognize the pump and dump is to understand its mechanism. If a relatively unknown currency’s value suddenly increases without reason, there is a manipulation possibility. It’s always best to do a little research before you buy and avoid rushing into a project before researching it.
The five factors that you should always keep in mind are:
- Monitor price movements
- Check the advertising source
- Monitor the trading volume
- Track market value
- Check the rules and regulations
Further, we will explain the abovementioned factors in detail.
Monitor price movements: One of the main characteristics of pumps and dumps is extreme price fluctuations. The value of an asset begins to increase rapidly for no discernible reason and declines just as rapidly with no apparent explanation. Looking at an asset’s price chart can provide much information about volume changes and price history. Some online trackers alert you to potential Pump and Dump schemes. For example, WalletInvestor tracks any increase of more than 5% within 5 minutes to alert users to potential scams.
Check the advertising source: Checking an asset’s information source is key to detecting Pump and dump schemes. When you see certain people promoting an asset or posting a lot about a less popular or high-risk asset, there is reason to be cautious. When an asset with a low market value is trending suddenly on Twitter or Facebook, one must consider the possibility of a scam. If an influencer with no financial market experience suddenly starts promoting an asset, consider the possibility of fraud. Many influencers may even promise guaranteed money back. Be wary of any promises of money and refunds.
Monitor trading volume: Low trading volume usually means low liquidity and an empty order list of buyers and sellers. It is easy for these assets to spike in price, especially in the short term. Any asset with a low-volume order list is more exposed to price manipulation.
Track the market value: The market value of an asset is calculated by multiplying its price by the amount of supply. Pump and dump groups often target assets with low market capitalization. These assets are subject to price manipulation by scammer groups. Although what counts as market value is subjective, properties with a market value under $1 million likely fall into this category.
Check the rules and regulations: Exchanges and brokers that do not have strict regulations are often more vulnerable to Pump and dump schemes. Analysis has shown that pump and dump schemes are relatively more dominant in Chinese exchanges compared to heavily regulated US-based exchanges. Often, price and volume increases occur on only one exchange.
Is There a Pump and Dump Indicator? Best Indicators to Detect Market Manipulation
Volume Indicators for Pump and Dump Detection
Volume is usually the first place manipulation leaves fingerprints, because pumps need aggressive participation to move price fast.
-
Volume spike vs baseline: Compare current volume to the 20–50 period average. If volume jumps 3–10x without a credible catalyst, treat it as a red flag—especially in low-liquidity markets.
-
OBV (On-Balance Volume): If price pushes to new highs but OBV flattens or drops, it can signal distribution (selling into the hype).
-
Volume Profile / Liquidity: Thin volume areas and “air pockets” mean weak support. If price breaks below a high-volume node after the pump, expect fast downside and higher slippage.
RSI and Momentum Indicators in Pump and Dump Scenarios
Momentum tools help you judge whether the move is overheating or losing energy—useful for avoiding late entries and timing exits.
-
RSI > 80 + parabolic candles: Don’t short just because RSI is high—use it as a risk filter: reduce size, tighten rules, or avoid fresh entries after oversized candles.
-
Bearish divergence: If price makes a higher high but RSI makes a lower high, the pump may be running out of fuel. Use a trigger like losing VWAP or breaking the prior swing low to confirm.
-
Rate of Change (ROC): A sudden ROC surge followed by flattening while price keeps rising often suggests the “easy” part of the pump is over.
Volatility Indicators to Spot Market Pump
Pumps distort volatility, and volatility indicators help you spot when conditions become abnormal and prone to sharp reversals.
-
ATR expansion: If ATR rapidly increases (e.g., doubles vs recent average), assume stop-hunts and whipsaws. Either widen stops with smaller size or skip the trade.
-
Bollinger Bands: A “band ride” up the upper band can persist, but the warning comes when price closes back inside the bands after an extended run—often a dump precursor.
-
Keltner Channels: If price repeatedly closes far outside the channel and then snaps back inside, treat it as exhaustion and avoid chasing.
Why No Indicator Can Predict Pump and Dump with 100% Accuracy?
Even the best pump and dump indicators only highlight probabilities, because manipulators can change tactics and timing once traders start reacting.
-
Indicators detect symptoms (abnormal volume, momentum, volatility), not intent.
-
News, exchange mechanics, and liquidity shifts can mimic pump signals.
-
Practical approach: require confluence (volume spike + momentum divergence + volatility expansion), then manage risk with smaller size, clear invalidation levels, and no chasing after parabolic candles.
How to avoid falling into the pump and dump trap
To avoid falling for a pump and dump scheme, you should be wary of scam offers and do your research.
Follow these rules to protect your capital:
Research on entering the financial markets and its basics before investing.
Before investing in markets such as forex and cryptocurrencies, it is essential to do thorough research. Additionally, be on the lookout for any warning signs, such as fake news or excessive hype on social media.
Use technical analysis to identify unusual price movements.
Technical analysis can be a valuable tool for detecting abnormal price and volume fluctuations in financial markets. Using pump and dump charts and indicators, you can analyze an asset’s price and volume data and identify unusual patterns or trends. For example, a sudden price increase or unusually high trading volume may indicate the existence of pump and dump pattern.
Avoid decisions driven by hype and FOMO.
One of the common ways investors fall victim to pump and dump schemes is by caving to hype and FOMO (fear of missing out). We recommend avoiding investing based solely on hype or FOMO for possible profit. Instead, make informed investment choices rooted in thorough research and analysis.
Read More: Trendo broker’s economic calendar analysis
How to protect your capital in case of pump and dump?
According to the above, entering the pump and dump schemes cannot be a suitable option for traders and investors who follow the principles of risk and capital management . However, every trader may experience mistakes and fall into the trap of these scams. The following principles will help this group of people to minimize their losses in this situation:
- Don’t rush to sell at a loss
- Ignore the media
- Accept the loss and try to minimize it
Further, we will briefly explain each principle.
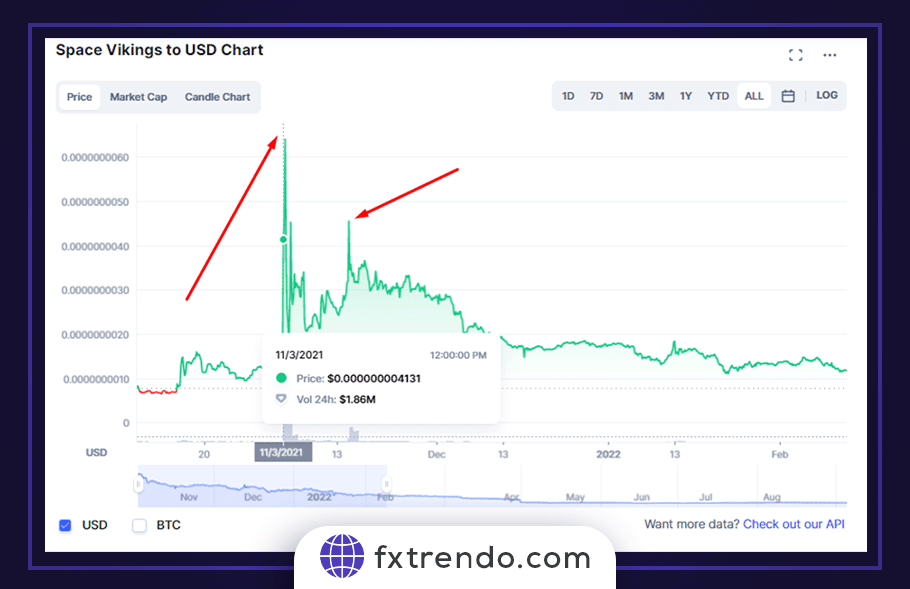
Don’t rush to sell at a loss: If you didn’t sell at the maximum price and the price drops and causes a loss, you have two options: sell at a minimum loss or wait for the second uptrend. If the asset is not a pure scam, there is an opportunity for a second pump and dump, which is weaker than the first wave but has a chance of success. For example, Space Vikings, which soared 600% in November 2011 following Elon Musk’s tweet, experienced half the growth of the previous pump two weeks after the dump.
Ignore the media: There will be a lot of conflicting information in the media, texting apps, and forums in the pump and dump background. Use logic instead of emotional decisions.
Accept the loss and try to minimize it: When you enter a pump and dump scheme, losing at least some capital is inevitable. From an emotional point of view, it is better to accept the loss and evaluate the situation with a clear mind
Summary
Anyone entering the financial markets needs to have a thorough understanding of market pump and dump schemes, use for pump trading. While these schemes are illegal in regulated financial markets such as forex, the lack of regulation in markets such as cryptocurrencies means these schemes can increasingly occur. So, be aware of the risks and information before engaging in any activity in these markets and get the necessary information. You should have a detailed capital management plan and always implement it.