When it comes to investing, two major markets often come into focus: Forex and global stocks.
The Forex market, short for foreign exchange, is where currencies are traded. It’s the largest financial market in the world, operating 24 hours a day, five days a week.
On the other hand, the global stock market involves buying and selling shares of companies from around the world. This market is influenced by company performance, economic indicators, and investor sentiment.
This blog provides a clear guide to the Forex and global stock markets. We’ll explore their key characteristics, compare their advantages and disadvantages, and discuss how they influence each other.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have a solid understanding of both markets and be better equipped to navigate the world of investing. Let’s dive in!
What is Forex?
Forex, or foreign exchange, is the global market for trading currencies, with a daily volume over $6 trillion. Unlike centralized stock markets, Forex trading is over-the-counter (OTC), conducted directly between parties via electronic platforms.
Participants include banks, financial institutions, corporations, governments, and individual traders, who trade currencies for international trade, hedging, or speculation.
Forex trading involves buying one currency and selling another, quoted in pairs like EUR/USD. The first currency is the base, and the second is the quote. The pair’s price shows how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
The Forex market operates 24/5, starting in the Asia-Pacific, moving to Europe, and ending in North America, allowing continuous trading and reaction to global events.
What are Global Stocks?
Global stocks represent shares of ownership in companies listed on stock exchanges worldwide. Buying a stock means owning a part of that company, giving you a claim on its assets and earnings. These stocks come from companies in various countries, offering exposure to different economies.
Investing in global stocks diversifies portfolios beyond the home country, spreading risk. Performance in different regions may not be closely correlated, balancing overall investment performance.
Global stocks are influenced by economic indicators, political events, and company-specific news. Changes in government policy, company innovations, and global economic trends like trade policies or interest rates can impact stock prices.
Trading occurs on major exchanges like NYSE, LSE, and TSE, providing a platform for buyers and sellers, ensuring transparency and liquidity.
Similarities between the Forex Market and Global Stock Market
While the Forex market and global stock market have distinct characteristics, they also share several similarities that can help investors understand their dynamics better.
1. E-commerce
Both markets are fully electronic, allowing traders to access and trade from anywhere in the world. Modern platforms, brokers, and exchanges are highly active online, offering dedicated applications and seamless access for users. Trendo broker stands out by providing traders worldwide with a specialized platform featuring low spreads and minimal trading commissions. By registering with Broker Trendo, you too can take advantage of these exceptional services.
2. Influence of Economic Indicators
Economic indicators play a crucial role in both markets. Data such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation can impact currency values in the Forex market and stock prices in the global stock market. Investors closely monitor these indicators to make informed trading decisions.
3. Impact of Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as elections, trade agreements, and conflicts, can significantly influence both markets. Such events can create volatility, leading to rapid price movements in currencies and stocks. Traders in both markets need to stay informed about global news to anticipate potential impacts.
4. Use of Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Traders in both markets use technical and fundamental analysis to guide their decisions. Technical analysis involves studying price charts and patterns to predict future movements, while fundamental analysis focuses on economic data, company performance, and other factors to assess value.
5. Risk and Profitability
Both markets come with their own unique risks, and traders may encounter substantial profits or losses. Effective risk management is essential for success in both. Capital management in forex requires extra caution to avoid overexposure. In contrast, the stock market often demands a focus on long-term strategies for sound money (capital) management.
6. Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, or the overall attitude of investors towards a particular market, affects both Forex and global stocks. Positive sentiment can drive prices up, while negative sentiment can lead to declines. Understanding market sentiment helps traders gauge potential market movements.
By recognizing these similarities, investors can better navigate the complexities of both the Forex and global stock markets. Whether trading currencies or stocks, a solid grasp of these common factors can enhance trading strategies and decision-making.
Read more: Everything about Dow Jones and its symbols in Forex
What are Key Differences between Forex and Global Stocks?
Understanding the key differences between Forex and global stocks is essential for making informed investment decisions. Here are the main distinctions:
1.Market Structure
Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to its global nature. Trading sessions overlap across different time zones, allowing continuous trading. Global stock markets, however, have specific opening and closing times based on their respective time zones, limiting trading hours.
2. Trading Hours
Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to its global nature. Trading sessions overlap across different time zones, allowing continuous trading. Global stock markets, however, have specific opening and closing times based on their respective time zones, limiting trading hours.
3. Liquidity
The Forex market is the most liquid financial market, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. This high liquidity means that large trades can be executed with minimal price impact. Global stock markets have lower liquidity compared to Forex, and liquidity can vary significantly between different stocks.
4. Volatility
Forex markets can be highly volatile, influenced by geopolitical events, economic data releases, and central bank policies. While global stocks can also be volatile, their price movements are often driven by company-specific news, earnings reports, and broader economic trends.
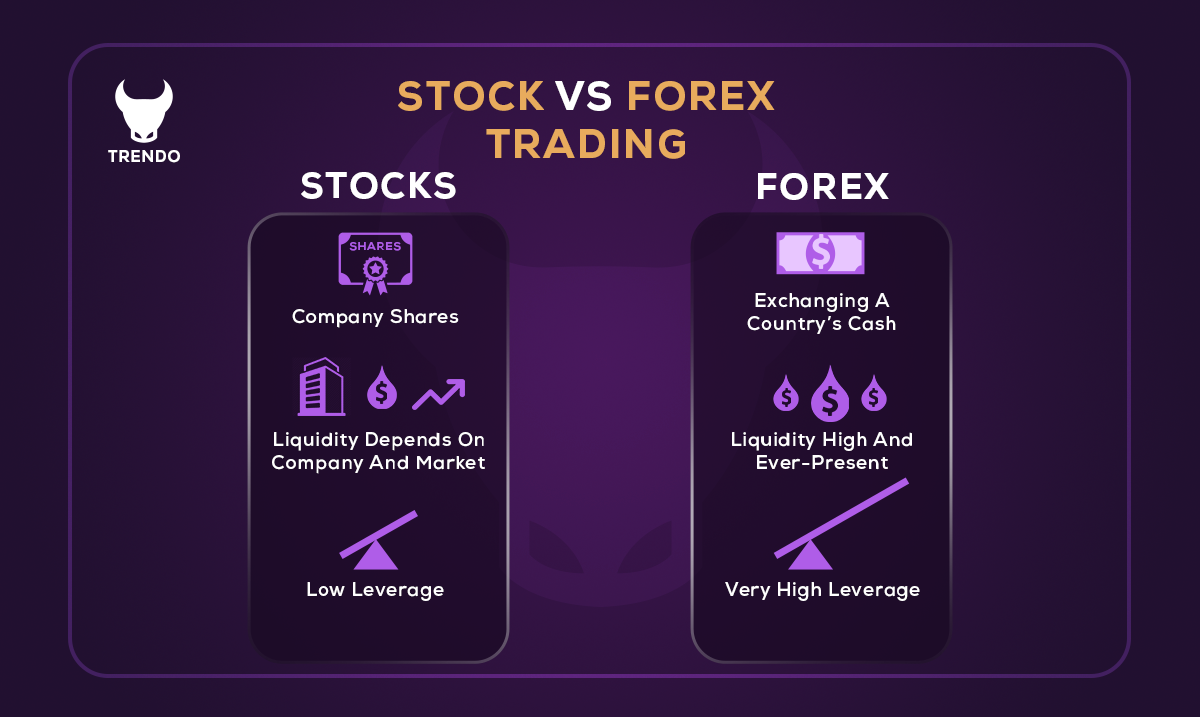
5. Leverage
Forex trading typically offers higher leverage compared to stock trading. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, amplifying both potential profits and losses. Stock trading also offers leverage, but it is generally lower and more regulated.
6. Investment Horizon
Forex trading is often short-term, with traders looking to capitalize on small price movements within minutes, hours, or days. In contrast, investing in global stocks is usually more long-term, with investors holding shares for months or years to benefit from company growth and dividends.
7. Market Influences
Forex prices are primarily influenced by macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and political stability. Global stock prices are affected by company performance, industry trends, and economic indicators. While both markets can be impacted by global events, the specific drivers of price movements differ.
Whether you prefer the fast-paced nature of Forex or the long-term growth potential of global stocks, knowing these distinctions will help you navigate each market more effectively.
What Are the Correlations Between Forex and Global Stock Markets?
Understanding the correlations between Forex and global stock markets can provide valuable insights for investors. Here are some key points to consider:

1. Economic Indicators
Both Forex and global stock markets are influenced by economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation. Positive economic data can boost investor confidence, leading to a rise in stock prices and a stronger currency. Conversely, negative data can have the opposite effect.
2. Interest Rates
Central banks play a crucial role in both markets by setting interest rates. Higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency and potentially boosting stock markets. Lower interest rates can have the opposite effect, weakening the currency and impacting stock prices.
3. Risk Sentiment
Market sentiment, or the overall mood of investors, affects both Forex and global stocks. During times of economic stability, investors may seek higher returns in stocks, leading to a stronger currency. In contrast, during periods of uncertainty, investors might flock to safe-haven currencies like the US dollar, impacting both markets.
4. Trade Relations
Trade relations between countries can influence both markets. Positive trade agreements can boost investor confidence, leading to higher stock prices and a stronger currency. Trade disputes or tariffs can create uncertainty, negatively affecting both markets.
5. Capital Flows
Capital flows refer to the movement of money for investment purposes. When investors move capital into a country, it can strengthen the currency and boost the stock market. Conversely, capital outflows can weaken the currency and negatively impact stock prices.
6. Corporate Earnings
While corporate earnings primarily impact stock prices, they can also influence Forex markets. Strong earnings reports can boost investor confidence in a country’s economy, leading to a stronger currency. Weak earnings can have the opposite effect.
7. Global Events
Global events such as political elections, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions can create volatility in both markets. Investors need to stay informed about global news to anticipate potential impacts on currencies and stocks.
By understanding these correlations, investors can better predict market movements and develop more effective trading strategies.
How Forex and Global Stocks Interact?
The interaction between Forex and global stock markets is complex and multifaceted. Here are some key ways in which these two markets influence each other:
Currency Valuations and Corporate Earnings
When a country’s currency strengthens, its exports become more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially reducing sales for companies that rely heavily on exports. This can negatively impact their stock prices. Conversely, a weaker currency can boost exports by making them cheaper, potentially increasing corporate earnings and driving up stock prices.
Foreign Investment Flows
Foreign investors often need to convert their home currency into the local currency of the country where they are investing. For example, if investors are buying U.S. stocks, they need to convert their currency into U.S. dollars. This demand for the local currency can strengthen it. Conversely, when investors sell off their investments and convert the proceeds back into their home currency, it can weaken the local currency.
Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rate changes by central banks can affect both Forex and stock markets. Higher interest rates can attract foreign capital, strengthening the currency and potentially boosting stock markets due to increased investment. Lower interest rates can have the opposite effect, leading to a weaker currency and potentially lower stock prices.
Economic Data Releases
Economic data releases, such as GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates, can impact both markets. Positive economic data can boost investor confidence, leading to a stronger currency and higher stock prices. Negative data can have the opposite effect, weakening the currency and lowering stock prices.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as elections, trade negotiations, and conflicts, can create uncertainty and volatility in both markets. For example, political instability in a country can lead to a sell-off in its stock market and a depreciation of its currency. Conversely, positive geopolitical developments can boost both the currency and stock market.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, or the overall mood of investors, can drive both Forex and stock markets. During times of optimism, investors may seek higher returns in stocks, leading to a stronger currency. During times of pessimism, investors may flock to safe-haven assets, such as the U.S. dollar or gold, impacting both markets.
Trade Balances
A country’s trade balance, which is the difference between its exports and imports, can influence both its currency and stock market. A trade surplus (more exports than imports) can strengthen the currency and boost stock prices, while a trade deficit (more imports than exports) can weaken the currency and negatively impact stock prices.
Pros and Cons of Trading Forex
Trading Forex offers several advantages and disadvantages that investors should consider before entering the market.
Pros
1. High Liquidity: The Forex market is the most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. This high liquidity ensures that trades can be executed quickly and with minimal price impact.
2. 24-Hour Market: Forex trading operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing traders to participate at any time. This continuous trading schedule provides flexibility for those with varying schedules and time zones.
3. Leverage Opportunities: Forex brokers often offer high leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify potential profits, making Forex trading attractive to those looking to maximize returns.
4. Low Transaction Costs: Transaction costs in the Forex market are generally low, primarily due to tight bid-ask spreads. This makes it cost-effective for traders to enter and exit positions frequently.
5. Diverse Trading Options: Forex trading involves a wide range of currency pairs, providing numerous opportunities for traders to find profitable trades. Additionally, traders can speculate on both rising and falling markets, increasing the potential for profit.
Cons
1. High Volatility: The Forex market can be highly volatile, with rapid price movements influenced by economic data, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. This volatility can lead to significant losses if not managed properly.
2. Leverage Risks: While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses. Traders using high leverage must be cautious and employ risk management strategies to protect their capital.
3. Complex Market Dynamics: The Forex market is influenced by a wide range of factors, including economic indicators, interest rates, and political events. Understanding these dynamics requires continuous learning and analysis, which can be challenging for beginners.
4. Potential for Overtrading: The 24-hour nature of the Forex market can lead to overtrading, where traders make excessive trades in an attempt to capitalize on every market movement. Overtrading can result in increased transaction costs and emotional stress.
5. Lack of Regulation: The decentralized nature of the Forex market means it is less regulated compared to stock markets. This can expose traders to risks such as fraud and unreliable brokers. It’s essential to choose reputable brokers and conduct thorough research before trading.
Pros and Cons of Trading Global Stocks
Trading global stocks offers various advantages and disadvantages that investors should consider.
Pros
1. Diversification: Investing in global stocks allows for diversification across different economies and industries. This can reduce risk, as poor performance in one market may be offset by gains in another.
2. Growth Opportunities: Global stocks provide access to emerging markets with high growth potential. Investing in companies from developing countries can offer significant returns as these economies expand.
3. Currency Exposure: Trading global stocks can provide exposure to different currencies. This can be beneficial if the investor’s home currency is weakening, as gains in foreign currencies can enhance overall returns.
4. Access to Leading Companies: Investing globally allows access to some of the world’s leading companies that may not be available in the investor’s home market. This includes multinational corporations with strong growth prospects.
5. Economic Cycles: Different countries experience economic cycles at different times. By investing globally, investors can take advantage of these varying cycles to optimize their returns.
Cons
1. Currency Risk: While currency exposure can be a benefit, it also introduces risk. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the value of investments, potentially leading to losses.
2. Political and Economic Risks: Investing in global stocks exposes investors to political and economic risks specific to each country. Changes in government policies, political instability, or economic downturns can negatively affect stock prices.
3. Regulatory Differences: Different countries have varying regulations and standards for financial markets. This can create challenges in understanding and complying with local laws, potentially increasing the complexity of investing.
4. Market Accessibility: Not all global markets are easily accessible to individual investors. Some markets may have restrictions on foreign investment or require significant capital to enter.
5. Information Asymmetry: Investors may have limited access to information about foreign companies compared to domestic ones. This can make it harder to conduct thorough research and make informed investment decisions.
Which Market Is Right for You?
Deciding between Forex and global stocks depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and trading style. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Investment Goals
If your goal is short-term profit, Forex might be more suitable due to its high liquidity and 24-hour trading. Forex allows for quick trades and the potential for rapid gains. On the other hand, if you’re looking for long-term growth and stability, global stocks may be a better fit. Stocks offer the potential for dividends and capital appreciation over time.
2. Risk Tolerance
Forex trading can be highly volatile, with significant price swings influenced by economic data and geopolitical events. If you have a high risk tolerance and can handle potential losses, Forex might be appealing. Conversely, if you prefer a more stable investment with less volatility, global stocks might be more appropriate. Stocks can still be volatile, but they often provide more predictable returns over the long term.
3. Trading Style
Active traders who enjoy analyzing market trends and making frequent trades might find Forex more engaging. The Forex market’s continuous operation allows for constant trading opportunities. If you prefer a more passive approach, investing in global stocks might be better. Stocks can be held for longer periods, requiring less frequent monitoring and trading.
4. Market Knowledge
Consider your familiarity with each market. Forex trading requires an understanding of currency pairs, economic indicators, and geopolitical factors. If you have experience or interest in these areas, Forex might be suitable. Global stocks require knowledge of company performance, industry trends, and economic conditions. If you are more comfortable analyzing companies and industries, stocks might be a better choice.
5. Leverage and Capital
Forex trading often involves high leverage, allowing you to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify both gains and losses. If you have limited capital but are comfortable with high leverage, Forex might be attractive. Global stocks typically require more capital to achieve significant returns, but they also offer lower leverage and potentially lower risk.
6. Diversification
If diversification is important to you, global stocks offer the ability to spread investments across different countries and industries. This can help mitigate risk and take advantage of growth opportunities in various markets. Forex trading, while offering diverse currency pairs, may not provide the same level of diversification as investing in a broad range of global stocks.
Conclusion
The Forex market and the stock market are closely interconnected, and changes in one market can have direct impacts on the other. Understanding these interactions is crucial for traders to make informed decisions.
Ultimately, the choice between the Forex market and the stock market depends on the trader’s goals, knowledge, and capabilities. Both markets have their own opportunities and risks, and traders must make wise decisions.