To succeed in this competitive field, professional traders rely on three types of analysis in forex: technical, fundamental, and sentiment. These analytical methods act as powerful tools to predict market trends and make informed decisions.
However, many individuals enter the forex market without sufficient preparation or understanding. This lack of readiness often leads to significant losses, as they fail to grasp the importance of analysis and the strategies required for success. Mastering technical, fundamental, and sentiment analysis is not just an advantage—it’s essential for navigating the complexities of forex trading.
In this article, we will explore these three types of analysis in forex, highlighting their benefits and limitations. By understanding their role and application, you can take a decisive step toward becoming a confident and informed forex trader.
Stay with us as we uncover the foundations of effective trading.
Types of Analysis in Forex
Understanding and mastering the different types of analysis in forex is essential for making sound decisions and maximizing success. Each method offers a unique perspective on the market, enabling traders to interpret trends, identify opportunities, and manage risks effectively.
The three types of analysis in forex are technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and sentiment analysis. Let’s explore each one in detail:
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is one of the most widely used types of analysis in forex for evaluating financial markets, including forex, stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and even real estate. This approach relies on studying historical price movements and chart patterns, operating on the belief that all the necessary information for predicting future prices is embedded within the charts. Technical analysts follow three core principles:
1. Price Reflects All Information: Market prices account for all available information, including fundamental and psychological factors, which are types of analysis in forex.
2. Trends Persist: Prices tend to move in trends, and changes in direction are often gradual and predictable.
3. History Repeats Itself: Past price patterns and behaviors are likely to recur, providing insights into future movements.
Let’s delve deeper into key aspects of technical analysis:
1. Price Action
Price action is a favored method in technical analysis, as types of analysis in forex, that relies on analyzing market demand and supply directly on charts. By identifying support and resistance levels, traders can anticipate price movements without relying heavily on external tools.
Several price action strategies have gained popularity among traders, including:
- Lance Beggs Method
- Nial Fuller Style
- Supply and Demand (Alfonso Moreno)
- Sam Seiden’s Approach
- RTM (Read the Market)
- ICT (Inner Circle Trader)
- Richard Wyckoff’s Principles
- Al Brooks Method
- Smart Money Concepts
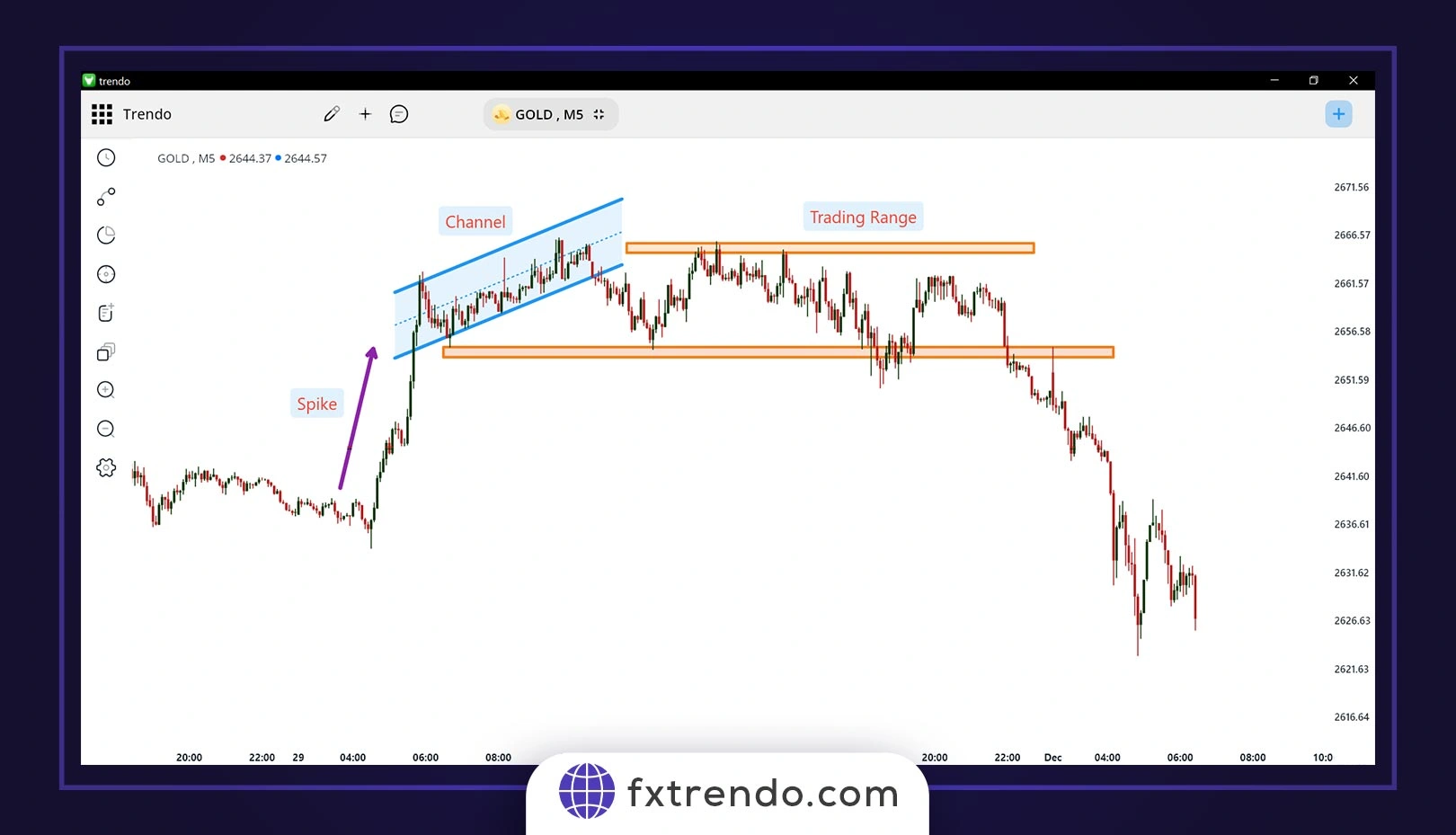
For example, in the image below you can see the AL BROOKS price action cycle on the gold chart (XAUUSD), this cycle consists of three parts: spike, channel, and trading range:
While mastering all these styles is unnecessary, focusing on one or two approaches and practicing consistently can yield significant results.
2. Indicators
Indicators are supportive tools that help traders pinpoint entry and exit points or identify crucial levels such as support and resistance. While indicators are often used alongside other strategies, some traders use them as their primary tools, considered as types of analysis in forex.
Popular indicators include:
RSI (Relative Strength Index): Highlights overbought or oversold conditions.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Measures momentum and trend direction.
Bollinger Bands: Identifies volatility and potential reversal zones.
Ichimoku Kinko Hyo: Provides a comprehensive view of trends and support/resistance levels.
CCI (Commodity Channel Index): Detects cyclical trends in price movements.
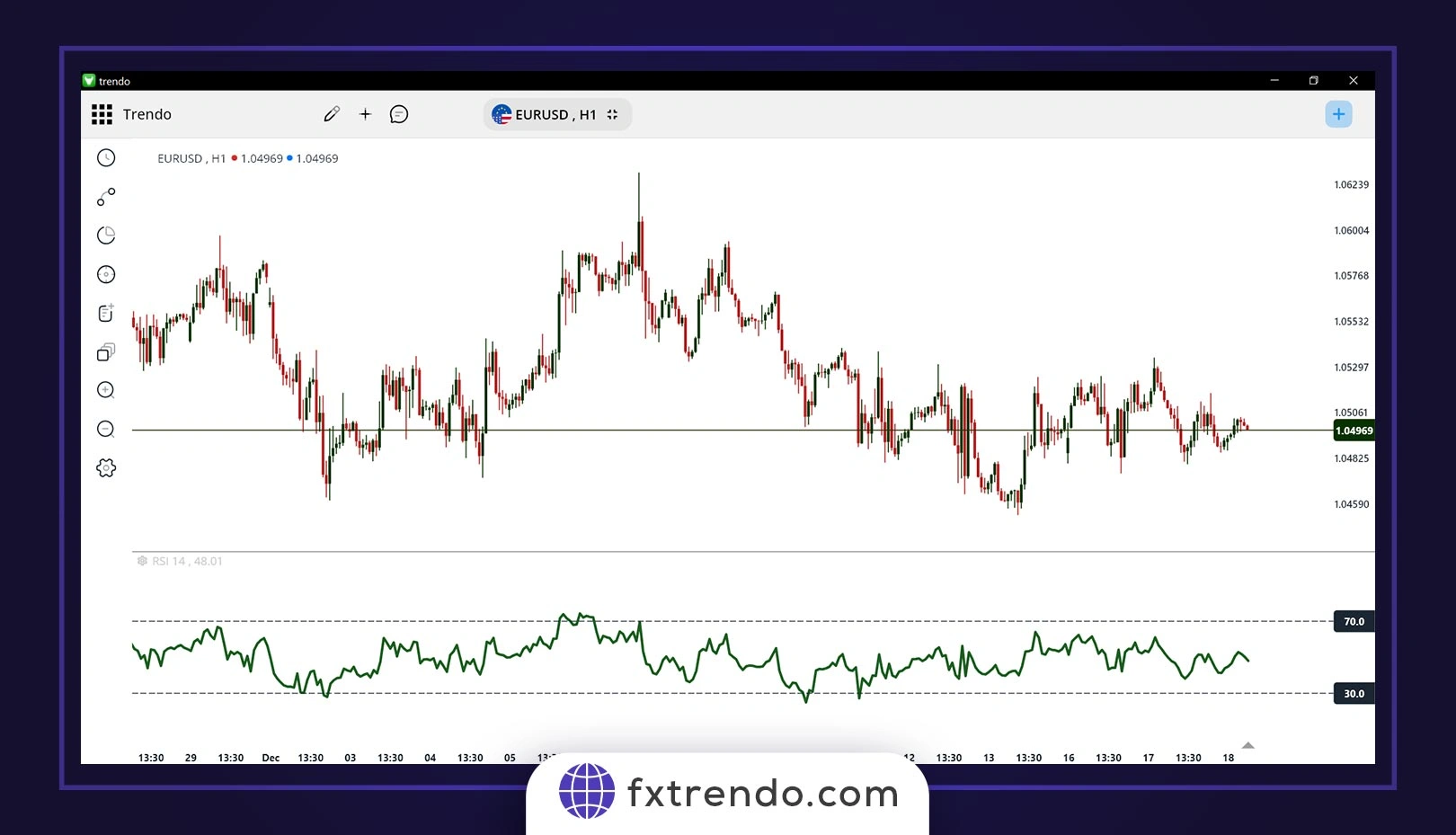
For example, in the image below of the EURUSD currency pair on the one-hour timeframe, you can see the RSI indicator. Traders use this indicator to find overbought and oversold points:
Although indicators are considered as types of analysis in forex and can enhance analysis, they are not foolproof and may occasionally generate false signals. Therefore, it’s best to use them as supplementary confirmation tools rather than standalone solutions.
3. Other Technical Analysis Methods
Beyond price action and indicators as types of analysis in forex, other techniques such as chart patterns, harmonic analysis, and Elliott Wave Theory are also widely used. Each method offers unique tools and principles for understanding market movements, catering to traders with different preferences and goals.
Key Considerations in Technical Analysis
1. The price chart is the foundation of technical analysis ,as types of analysis in forex, with tools like indicators and trading systems layered on top.
2. Mastery of technical analysis requires consistent practice and familiarity with various tools and strategies.
3. Emotional discipline is crucial; traders should adhere to their strategies and avoid impulsive decisions.
4. No technical analysis method guarantees success, so risk management is essential to mitigate potential losses.
By developing a solid understanding of technical analysis and honing your skills, you can better navigate the complexities of the forex market and make more informed trading decisions.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a critical types of analysis in forex for evaluating financial markets, including forex, by examining the economic, political, and social factors that influence asset prices. Unlike technical analysis, which focuses on historical price data, fundamental analysis delves into the underlying causes of price movements. Both of them are types of analysis in forex that are necessary. This approach assumes that the intrinsic value of an asset is shaped by fundamental economic conditions and forces. By using this method, traders can gain a long-term perspective on the market and anticipate potential price changes.
Here are some of the key tools and factors used in fundamental analysis:
Economic Indicators
Economic reports, such as inflation rates, unemployment figures, and Gross Domestic Product (GDP), provide valuable insights into the economic health of a country. These indicators can signal whether a currency is likely to strengthen or weaken over time.
Interest Rates
Central banks’ decisions to raise or lower interest rates significantly impact currency values. For instance, an increase in interest rates typically strengthens a currency as it attracts more foreign investment seeking higher returns.
Political and Geopolitical Events
Elections, policy changes, sanctions, and conflicts can cause sharp movements in the forex market. Such events often create uncertainty, which directly affects market behavior and currency valuations.
Economic Calendars
Traders rely on economic calendars to track the release of key economic data. These tools provide the scheduled release times, forecasts, and actual figures of crucial reports, helping traders prepare for potential market reactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fundamental Analysis
Like any trading approach, fundamental analysis, as types of analysis in forex, has its strengths and weaknesses:
Advantages
Accurate Long-Term Insights: Fundamental analysis is highly effective for long-term market forecasting, offering a broader understanding of price movements over time.
Intrinsic Value Assessment: This method helps traders identify the true value of an asset and compare it to its current market price, revealing potential overvalued or undervalued opportunities.
Disadvantages
Complexity: Fundamental analysis requires deep knowledge of economics and political factors, making it more challenging and time-consuming compared to technical analysis.
Short-Term Volatility: In the short term, prices may behave unpredictably, even contradicting fundamental factors, which can be confusing for traders.
Practical Example of Fundamental Analysis in Forex
Imagine the U.S. Federal Reserve announces an increase in interest rates. This decision typically strengthens the U.S. dollar as investors seek higher returns, making USD-based assets more attractive. Consequently, the EUR/USD currency pair may decline as the dollar gains strength against the euro.
A trader using fundamental analysis, as one types of analysis in forex, could anticipate this change and open a sell position on EUR/USD, potentially profiting from the market movement. However, it’s essential to note that the market’s reaction to news is as important as the news itself. For instance, even positive data can lead to unexpected price movements if the market has already priced in the information.
Therefore, combining fundamental analysis with technical tools can offer a more comprehensive view of how data and news influence market behavior, helping traders make more informed decisions.
For complete information and to view fundamental analysis tutorials, as types of analysis in forex, please refer to the fundamental analysis tutorial link.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis, as a types of analysis in forex, is the art of studying the collective psychology of traders in the market, and one of the most practical types of analysis in forex. This approach aims to identify the overall mood of the market—whether it is optimistic (bullish) or pessimistic (bearish). The foundation of sentiment analysis is the understanding that collective emotions, even if irrational, can significantly influence market trends and price movements.
Market sentiment provides unique insights that complement technical and fundamental analysis. It helps traders gauge the prevailing attitude of the majority, enabling them to anticipate potential market reversals or continuations. However, interpreting market sentiment can be challenging due to its fluid nature, as it is often influenced by sudden news or economic events.
Tools Used in Sentiment Analysis
To effectively measure market sentiment, as types of analysis in forex, traders rely on several key indicators:
Commitments of Traders (COT) Report
The COT report provides detailed insights into the positions of large market participants, such as institutional traders and hedge funds. By analyzing this data, traders can identify whether the majority are leaning towards long (buy) or short (sell) positions, which may indicate overbought or oversold conditions. It makes sentiment analysis, which is one of the main types of analysis in forex, more effective.
Fear and Greed Index
This index measures the level of fear or greed in the market, considered as types of analysis in forex, providing a snapshot of the current emotional state of traders. Extreme fear might signal undervaluation, while extreme greed can indicate overvaluation.
VIX (Volatility Index)
Known as the “fear index,” the VIX measures market volatility expectations. A high VIX value typically reflects heightened market uncertainty or fear, while a low VIX suggests stability and confidence, considered as types of analysis in forex.
Advantages of Sentiment Analysis
1. Identifying Market Extremes: Sentiment analysis, as types of analysis in forex, helps traders spot overbought or oversold conditions, often signaling potential reversals. For example, if sentiment indicators show excessive optimism, it could mean the market is nearing a peak.
2. Complementary Insights: This analysis fills the gaps left by technical and fundamental approaches, as types of analysis in forex, offering a broader perspective on market behavior.
3. Predicting Short-Term Movements: Sentiment-driven price moves, such as sharp reactions to unexpected news, can provide trading opportunities for short-term gains.
Challenges of Sentiment Analysis
1. Limited Data Sources: Compared to technical and fundamental analysis, sentiment analysis has fewer dedicated tools and data sources, making it less straightforward to apply.
2. Rapid Changes in Sentiment: Market sentiment can shift quickly in response to new information, making its predictions less reliable for long-term strategies.
3. Dependency on Context: Sentiment analysis rarely works in isolation. It needs to be combined with other analytical methods to provide actionable insights.
How to Use Sentiment Analysis?
Due to the importance of sentiment analysis as types of analysis in forex, learn to use it effectively is vital. For instance, suppose the COT report reveals that a significant number of institutional traders have taken long positions on the U.S. dollar. While this suggests optimism about the dollar, it might also indicate that the currency is approaching overbought levels, increasing the likelihood of a correction.
Similarly, during the release of major economic data, market sentiment can lead to rapid price movements. For example, if a negative economic report is unexpectedly released, it may instill fear in the market, causing a widespread sell-off—even if the underlying fundamentals suggest stability.
Sentiment analysis is rarely used as a standalone strategy, as the emotional state of the market can change abruptly due to technical or fundamental factors. To achieve a well-rounded trading perspective, traders often combine sentiment analysis with technical and fundamental insights, ensuring more balanced and informed decision-making.
Comparison of Forex Analysis Types
Traders primarily use three types of analysis in forex: technical, fundamental, and sentiment. Each provides a different lens on market dynamics, and choosing the right one—or combining them—depends on your trading style and goals.
Technical analysis studies price charts, patterns, and indicators to forecast short-term moves.
Fundamental analysis evaluates economic data, interest rates, and geopolitical events for long-term currency valuation.
Sentiment analysis measures market psychology through positioning data and fear/greed gauges to spot extremes.
No method stands alone as the best. Technical excels in timing, fundamental in direction, and sentiment in spotting reversals. Many professionals integrate all three types of analysis in forex for higher-probability setups, reducing blind spots from relying on one approach.
The following table provides the details of each of the three types of analysis in forex.
| Type of Analysis | Timeframe | Best for | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Analysis | Short to medium-term (minutes to weeks) | Timing entries/exits, trend identification | Visual and rule-based; works across all conditions; precise levels | Lags real-time events; ignores macro drivers; false signals in ranging markets |
| Fundamental Analysis | Long-term (months to years) | Directional bias, macro trends | Explains “why” prices move; strong for carry trades and positioning | Poor for precise timing; overwhelmed by short-term noise; requires deep economic knowledge |
| Sentiment Analysis | Short-term (days to weeks) | Spotting extremes, contrarian plays | Reveals crowd overreactions; early reversal warnings | Rapidly shifting; limited standalone tools; often needs confirmation from other methods |
What Is the Best Analysis for the Forex Market?
The forex market, with its dynamic and ever-changing nature, demands deep knowledge and insightful strategies to make informed decisions. As discussed, the three primary types of analysis in forex—technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and sentiment analysis—each have their strengths and limitations.
No One-Size-Fits-All Approach
No single method can fully capture the complexity of the forex market. Each type of analysis offers a unique perspective:
Technical Analysis, as one of the primary types of analysis in forex, is excellent for identifying price trends and key levels, but it doesn’t account for external economic or political events.
Fundamental Analysis, as the second primary types of analysis in forex, provides insights into the underlying economic and geopolitical factors driving currency values but may not help with precise entry or exit points.
Sentiment Analysis, as the third primary types of analysis in forex, helps gauge the overall mood of the market, highlighting potential extremes, yet it relies on rapid and often unpredictable shifts in emotions.
For these reasons, relying solely on one approach can leave traders vulnerable to missing important aspects of the market’s behavior.
The Power of Combining Methods
The most effective traders often blend these types of analysis in forex into a comprehensive strategy. Here’s how combining them can lead to better outcomes:
1. Integrating Fundamentals and Technicals: Fundamental analysis can guide traders on which currency pairs to focus on based on macroeconomic trends or central bank policies. Technical analysis can then help pinpoint the optimal entry and exit points within that context. For instance, if a country raises interest rates (a bullish signal for its currency), traders can use technical indicators like support and resistance levels to execute their trades strategically.
2. Incorporating Sentiment Analysis: Understanding market sentiment can help traders gauge whether a trend is sustainable or overextended. For example, if technical and fundamental indicators suggest a bullish trend but sentiment tools like the Fear and Greed Index indicate extreme optimism, a correction might be imminent.
3. Balancing Long- and Short-Term Perspectives: Fundamental analysis often provides a long-term outlook, while technical analysis excels in short- to medium-term planning. Combining both ensures that trades are not only aligned with macroeconomic realities but also executed at the right time.
Key Takeaways
Technical analysts: should remain aware of fundamental events, as economic news and geopolitical developments can disrupt technical patterns.
Fundamental analysts: can refine their strategies by incorporating technical tools to identify precise trading levels.
All traders: should consider sentiment analysis to understand collective market behavior and anticipate potential turning points.
Ultimately, the “best” analysis depends on the trader’s goals, experience, and trading style. For long-term investors, fundamental analysis might take precedence, while day traders might rely more on technical and sentiment tools. The key is adaptability and the willingness to integrate multiple perspectives for a holistic understanding of the market.
By leveraging the strengths of all three types of analysis in forex, traders can better navigate the complexities of the forex market and improve their chances of success.
Which Forex Analysis Is Best for You?
Beginners
Start with technical analysis — it’s the most accessible and practical entry point. Focus on clean price action (support/resistance, trendlines) or 2-3 simple indicators (e.g., 50/200 EMA crossover + RSI). Trade one major pair like EUR/USD on a demo account. Practice identifying high-probability setups on higher timeframes (H4/D1) to avoid intraday noise. Skip fundamentals until you can read charts fluently — jumping into news trading early often leads to blown accounts.
Day Traders
Technical analysis is your core tool, but layer in sentiment for edge. Use lower timeframes (M15-H1) with price action around key levels, confirmed by indicators like Volume Profile or Order Flow if available. Before major news, check COT data or retail positioning (e.g., IG Client Sentiment) — if retail is heavily long into resistance, fade it. Avoid trading during high-impact releases unless your setup aligns perfectly; sentiment extremes help filter false breakouts.
Swing Traders
Combine technical for setups with fundamental for bias. Scan for confluences like a bullish pinbar at daily support while the currency benefits from rising rates or positive data differentials. Hold trades for days to weeks, trailing stops with ATR. Use sentiment (COT extremes) to avoid entering overextended moves — e.g., don’t go long GBP if specs are at record longs despite favorable fundamentals.
Long-Term Traders
Lead with fundamental analysis — build positions around interest rate differentials, growth outlooks, or geopolitical themes (e.g., carry trades in high-yield currencies). Use technical only for better entry pricing on weekly/monthly charts (e.g., wait for pullbacks to moving averages). Monitor sentiment via COT to scale in/out — extreme commercial hedging often signals macro turns worth respecting.
Can You Combine Different Types of Analysis in Forex?
Yes — combining different types of forex analysis strategies is not just possible; it’s the most practical and effective way to trade consistently. Relying on a single method creates blind spots that the market exploits.
Hybrid Trading Approach
A hybrid trading approach integrates technical, fundamental, and sentiment analysis to create high-conviction setups with multiple layers of confirmation. This reduces false signals, improves timing, and adapts to any market condition — ranging, trending, or news-driven.
Professionals rarely trade purely on one method. Instead, they use a structured workflow:
- Start with fundamentals for directional bias.
- Refine with technicals for precise entries/exits.
- Filter with sentiment to avoid crowded trades.
The result: fewer trades, but higher win rates and better risk/reward. Beginners often overcomplicate this — start by mastering two methods (e.g., technical + sentiment) before adding the third. Backtest hybrids on historical data to see how confluence filters out losing setups.
Fundamental + Technical
This is the most common and powerful hybrid. Fundamentals answer “why” a currency should move (interest rate differentials, GDP surprises, central bank policy shifts). Technicals answer “when” and “at what price” to enter.
Practical application:
- Identify a macro theme (e.g., Fed hiking rates while ECB cuts → USD strength).
- Wait for technical confirmation: pullback to support in an uptrend, bullish candle pattern, or indicator alignment (e.g., MACD crossover + price above 200 EMA).
- Enter only when both align — this avoids fighting the trend or entering too early on news spikes.
Real edge comes from patience: fundamentals can take weeks to play out, so use technicals to scale in on dips rather than chasing breakouts.
Sentiment as Confirmation
Sentiment analysis acts as an outstanding filter — it reveals crowd psychology and positioning extremes. Use it to confirm (or invalidate) your fundamental/technical setup.
Practical tools and rules:
- Check COT reports weekly: extreme speculator longs often signal tops; commercial hedging extremes signal bottoms.
- Monitor retail sentiment (IG, Myfxbook): fade when retail is >70% long/short at key levels.
- During high volatility (VIX spikes), extreme fear/greed can override short-term technicals.
Rule of thumb: if your technical + fundamental setup aligns but sentiment is at extremes against you, sit out or reduce size. Sentiment catches overextensions that pure chart reading misses.
Example
Here’s a real-world hybrid setup on EUR/USD:
- Fundamental bias: ECB signaling rate cuts while Fed holds steady → structural EUR weakness.
- Technical setup: Price rejects 1.1000 resistance zone on daily chart with bearish pinbar + RSI divergence; breaks trendline support.
- Sentiment confirmation: COT shows speculators at multi-year net longs; retail heavily long (80%+ per IG data) — classic overcrowding.
Trade execution: Short the retest of broken support, stop above 1.1000, target 1.0700–1.0800 zone. Risk 1%, trail with ATR once in profit.
This confluence made it a high-probability fade of the crowd.
The technical setup is provided in the following image:
Effective Forex Analysis Strategies
Having a clear strategy for types analysis in forex is essential for making informed and profitable decisions. The three main types of analysis in forex—technical, fundamental, and sentiment—each provide valuable insights into market behavior. To make the most of these methods, traders should combine them effectively. Here are key strategies for successful forex analysis:
1. Combine Technical, Fundamental, and Sentiment Analysis
One effective strategy is to blend all three types of analysis in forex. Relying on only one method can leave traders vulnerable to unforeseen market changes. By integrating technical, fundamental, and sentiment analysis, traders can get a complete view of the market.
Technical analysis: identifies price levels and trends, helping traders decide when to enter or exit a position.
Fundamental analysis: explains the factors influencing currency movements, providing context behind trends.
Sentiment analysis: shows market emotions, helping traders spot potential turning points when the market is overly optimistic or pessimistic.
Using all three types of analysis in forex together helps traders anticipate market shifts more accurately.
2. Focus on Key Economic Indicators
In fundamental analysis, it’s important to track key economic indicators that affect currency values. Reports such as GDP, unemployment rates, inflation, and interest rate decisions give insight into a country’s economic health.
For example, strong GDP growth and a low unemployment rate usually strengthen a currency. In contrast, rising inflation or a widening trade deficit could weaken a currency. Staying on top of these indicators can help traders predict currency movements. Thus, fundamental as types of analysis in forex is essential.
3. Master Support and Resistance Levels
In technical analysis, identifying support and resistance levels is crucial. These levels are where price movements tend to reverse. Support is the price level where demand increases, halting a downtrend, while resistance is where selling pressure prevents further price increases.
Traders use these levels to make decisions such as:
- Buying near support, expecting prices to rise.
- Selling near resistance, anticipating a price drop.
Mastering support and resistance helps traders improve timing and minimize risk.
4. Stay Informed About Global News and Events
Fundamental analysis, as one of the primary types of analysis in forex, involves tracking a wide range of global news events that can impact sentiment and market movements. Political events, natural disasters, and changes in government policies can cause sudden price shifts.
By staying updated on global news, traders can better understand potential market reactions and prepare for any unexpected changes. For example, central bank policy decisions or geopolitical tensions often lead to currency fluctuations, and traders who anticipate these events can react quickly.
5. Use Risk Management Tools
Effective analysis isn’t just about making accurate predictions; it’s also about managing risk. Even the best analysis can’t guarantee success, so traders should implement risk management strategies.
Traders should:
- Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Use proper position sizing to protect capital.
- Diversify trades to reduce exposure to a single currency pair.
Risk management tools help protect capital while taking advantage of trading opportunities.
6. Develop a Trading Plan
Clear trading plans are essential for successful forex analysis strategies. This plan should outline entry and exit strategies, risk tolerance, and the methods used for market analysis.
Traders should:
- Define their goals (short-term or long-term).
- Decide which types of analysis in forex to focus on, or combine them based on preference.
- Set risk-reward ratios to ensure potential rewards outweigh risks.
A trading plan helps traders stay disciplined and avoid impulsive decisions based on emotions.
7. Backtest and Refine Your Strategies
Before applying a new strategy, it’s important to backtest it with historical data. This helps traders assess how well the strategy would have performed in different market conditions. Backtesting also identifies weaknesses in a strategy, allowing for improvements before risking real capital.
Refining strategies based on backtesting results can increase accuracy and improve trading outcomes.
8. Practice Patience and Discipline
Successful forex trading requires patience and discipline. Traders must wait for favorable market conditions based on solid analysis rather than making impulsive decisions.
By sticking to a well-defined strategy and avoiding emotional reactions to short-term market moves, traders increase their chances of long-term success.
Effective forex analysis strategies require a combination of types of analysis in forex: technical, fundamental, and sentiment. By integrating these methods, staying informed about global events, and applying sound risk management, traders can make better decisions. Developing a clear trading plan and remaining disciplined helps traders navigate the complexities of the forex market with confidence.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Forex Analysis
Forex trading can be complex, and even experienced traders can make mistakes that impact their profitability. Avoiding common errors in each types of analysis in forex is key to improving your trading success. Below are some of the most common mistakes traders make and tips on how to avoid them.
1. Over Reliance on One Type of Analysis in Forex Trading
Relying too much on just one type of analysis in forex trading—whether it’s technical, fundamental, or sentiment analysis—is a common mistake. While each of these methods provides valuable insights, none of them can predict the market with 100% accuracy.
For example, focusing only on technical analysis may cause you to overlook important economic news that can impact the market. Similarly, relying solely on fundamental analysis might miss short-term price movements driven by technical factors. To get a clearer picture of the market, combine technical, fundamental, and sentiment analysis for more informed decisions.
2. Ignoring Risk Management
Failing to implement effective risk management strategies is another major mistake. Even with the best analysis, the forex market can be unpredictable, and losses are inevitable. Without proper risk management, traders risk losing their capital.
Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and ensure your position sizes align with your risk tolerance. Avoid overleveraging, which amplifies both gains and losses. Proper risk management helps protect your capital and ensures you can continue trading long-term.
3. Letting Emotions Drive Decisions
Many traders let emotions like fear, greed, and excitement influence their trading decisions, leading to poor outcomes. For example, fear may cause traders to exit a position too early, while greed might lead them to hold onto a position for too long, hoping for higher returns.
Stay disciplined and stick to your trading plan, regardless of emotions. Avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term price fluctuations. Focus on long-term goals and follow your analysis to guide your trades.
4. Overtrading or Undertrading
Both overtrading and undertrading are common mistakes. Overtrading occurs when traders take too many positions, often driven by the desire to make quick profits. This increases transaction costs and risk exposure. Undertrading happens when traders avoid taking positions out of fear or hesitation, missing profitable opportunities.
Find a balance between the two. Stick to your trading plan and take trades that align with your strategy. Avoid trading excessively and don’t hesitate when a good opportunity arises.
5. Neglecting to Stay Updated on Economic News
Economic events and geopolitical developments can significantly impact currency prices. Traders who fail to stay updated on important news, such as central bank decisions, inflation reports, or political events, risk being caught off guard by sudden market movements.
Follow a reliable economic calendar and set up notifications for key reports and events. Being aware of these events helps you make better decisions and adjust your trades accordingly.
6. Misinterpreting Indicators or Data
Many traders misinterpret indicators or economic data. For example, relying too heavily on technical indicators without considering the broader market context can lead to misleading conclusions. Similarly, using economic data out of context can result in incorrect predictions.
Understand how different indicators work and interpret them in relation to the overall market. For instance, while an RSI reading above 70 may indicate overbought conditions, it doesn’t guarantee a price reversal without other confirming factors like support or resistance levels.
7. Failing to Adapt to Changing Market Conditions
The forex market is constantly evolving, and strategies that work in one market environment may not be effective in another. Some traders make the mistake of sticking to one approach even when market conditions change.
Stay flexible and be willing to adjust your strategy based on current market conditions. For instance, if volatility is high due to global events, use a more conservative approach with tighter stop losses. Regularly assess the market and adjust your tactics accordingly.
8. Lack of a Trading Plan
Trading without a clear trading plan can lead to inconsistent results. A trading plan should outline your goals, risk tolerance, preferred analysis methods, and entry and exit strategies. Without a plan, traders are more likely to make emotional or reactive decisions.
Develop a detailed trading plan and stick to it. Regularly review your plan to ensure it remains relevant and aligns with your goals.
9. Ignoring the Importance of Backtesting
Backtesting is testing a strategy on historical data to see how it might perform. Many traders skip this step, which can lead to poor results in real-time trading.
Always backtest your strategies to understand how they might perform under different market conditions. This helps refine your approach and improves your chances of success.
Avoiding these common mistakes in forex analysis is essential for improving your trading performance. By combining different types of analysis in forex, implementing solid risk management strategies, staying updated on global news, and maintaining discipline, you can enhance your chances of success in the forex market.
Conclusion
Analysis is essential for understanding market movements and making informed decisions. Three main types of analysis in forex—technical, fundamental, and sentiment—each offer unique insights into market behavior, with their own strengths and limitations.
For beginner traders, it is recommended to start with technical analysis as a foundation, since it is more straightforward and quicker to grasp. As you gain experience, you can incorporate fundamental and sentiment analysis into your strategy.
Combining these three types of analysis in forex allows traders to take advantage of different market opportunities, manage risks better, and increase their chances of success.
If you want to deepen your understanding of forex analysis and improve your trading strategies, visit Trendo for more expert insights, resources, and tools. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your skills, Trendo offers valuable knowledge to help you navigate the forex market with confidence.