But what exactly is margin in forex trading? Simply put, margin is the amount of money a trader needs to deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. It acts as a good faith deposit, ensuring that traders can cover potential losses.
Unlike fees or costs, margin is a portion of your account balance set aside by your broker. This allows you to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, amplifying both potential gains and risks.
Understanding margin is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the forex market effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into everything you need to know about FX margin, from its basic principles to advanced strategies, helping you trade with confidence and precision.
Ready to unlock the secrets of forex margin? Let’s dive in!
What is Margin in Forex Trading?
Margin in forex trading is a fundamental concept that every trader needs to understand. Essentially, margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged trading position. It acts as a security deposit held by your broker to ensure that you can cover potential losses.
When you trade on margin, you are using leverage, which means you can control a larger position than what your actual capital would allow. For example, with a margin requirement of 1%, you can control a $100,000 position with just $1,000 of your own money. This leverage can amplify your profits, but it also increases the risk of significant losses.
Margin is not a fee or a cost; it is simply a portion of your funds set aside by the broker. This amount is “locked up” for the duration of the trade and is released once the position is closed. Understanding how margin works is crucial for managing risk and making informed trading decisions in the forex market.
How Margin in Forex Works?
Margin in forex trading is a crucial concept that allows traders to leverage their positions. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
When you decide to trade forex, you typically don’t need to pay the full value of the position you want to open. Instead, you deposit a fraction of the total value, known as the margin. This margin acts as a security deposit to cover potential losses.
For example, if you want to trade $100,000 worth of currency and your broker requires a 1% margin, you only need to deposit $1,000. The broker essentially lends you the remaining $99,000. This leverage enables you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital.
However, this also means that both your potential profits and losses are magnified. If the market moves in your favor, you can earn significant returns. Conversely, if the market moves against you, your losses can exceed your initial margin deposit.
To manage this risk, brokers monitor your margin level. If your account balance falls below a certain threshold, known as the maintenance margin, the broker may issue a margin call. This requires you to deposit additional funds to maintain your position. If you fail to do so, the broker may close your position to prevent further losses.
Understanding how margin works is essential for effective risk management in forex trading. It allows you to maximize your trading potential while being mindful of the risks involved.

Types of Margins in Forex Trading
Understanding the different types of margins in forex trading is essential for managing your trades effectively. Here are the key types of margins you need to know:
1. Initial Margin Requirement: This is the amount of money required to open a new position. It acts as a security deposit to cover potential losses. The initial margin is usually a small percentage of the total trade value, allowing traders to leverage their positions.
2. Maintenance Margin: Also known as the minimum margin, this is the minimum amount of equity that must be maintained in your trading account to keep your positions open. If your account balance falls below this level, you may receive a margin call from your broker, requiring you to deposit additional funds.
3. Used Margin: This is the portion of your account equity that is currently being used to maintain open positions. It represents the total amount of margin that has been “locked up” and is not available for opening new trades.
4. Free Margin: Free margin is the amount of equity in your account that is available for opening new positions. It is calculated by subtracting the used margin from your total equity. Free margin acts as a buffer to absorb potential losses from your open trades.
5. Margin Level: This is a percentage value that indicates the health of your trading account. It is calculated by dividing your equity by the used margin and multiplying by 100. A higher margin level indicates a healthier account, while a lower margin level may trigger a margin call.
How to Calculate Margin in Forex Trading?
Calculating margin in Forex trading is a crucial skill that every trader should have. It helps you understand the amount of capital required to open and maintain a trading position. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide on how to do it:
1. Identify the Currency Pair: The first step is to determine the currency pair you want to trade. This could be any pair like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, etc.
2. Determine the Lot Size: The lot size refers to the number of units of the base currency in the pair that you are trading. The standard lot size in forex trading is 100,000 units, but there are also mini (10,000 units), micro (1,000 units), and nano (100 units) lot sizes available.
3. Determine the Leverage: Leverage is the ratio between the trader’s capital and the position size. It allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. For instance, if the leverage is 1:100, it means that for every $1 of capital, the trader can control $100 in the market.
4. Calculate the Margin: The formula to calculate margin in forex trading is quite simple:

Let’s break down each component of the formula:
Lot Size: The number of units of a currency pair that you are trading.
Contract Size: The value of one lot in the base currency. For example, if you are trading the EUR/USD pair, the contract size would be 100,000 euros.
Leverage: The ratio between the trader’s capital and the position size.
For example, if you want to buy 1 lot (100,000 units) of the EUR/USD pair, and the leverage offered by your broker is 1:50, the margin would be:

In this example, you would need 2,000 euros as margin to open the position. Remember, trading on margin can significantly increase your profits, but it also exposes you to greater potential losses.
So, it’s important to use margin wisely and maintain a healthy margin level at all times.
How Much Margin Do I Need? What is the Required Margin in Forex?
Determining how much margin you need in forex trading depends on several factors, including the leverage offered by your broker, the currency pair you are trading, and the size of your position. Here’s a simple guide to help you understand the required margin:
1. Leverage: Leverage allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. For example, if your broker offers a leverage of 1:100, you can control $100,000 with just $1,000. The higher the leverage, the lower the margin requirement.
2. Currency Pair: Different currency pairs have different margin requirements. Major pairs like EUR/USD typically have lower margin requirements compared to exotic pairs. This is because major pairs are more liquid and less volatile.
3. Position Size: The size of your trade also affects the required margin. Larger positions require more margin. For instance, trading one standard lot (100,000 units) will require more margin than trading one mini lot (10,000 units).
4. Margin Requirement Calculation: The required margin is usually expressed as a percentage of the total trade value. For example, if the margin requirement is 1%, and you want to trade $100,000, you need to deposit $1,000 as margin.
The Role of Leverage in Margin Trading
Leverage in forex trading refers to the use of borrowed funds to increase the size of a trading position beyond what would be possible with just your own capital. Essentially, leverage allows traders to control a larger amount of currency with a smaller initial investment. For example, with a leverage ratio of 1:100, you can control $100,000 worth of currency with just $1,000 of your own money. This amplifies both potential profits and potential losses, making it a powerful but risky tool.
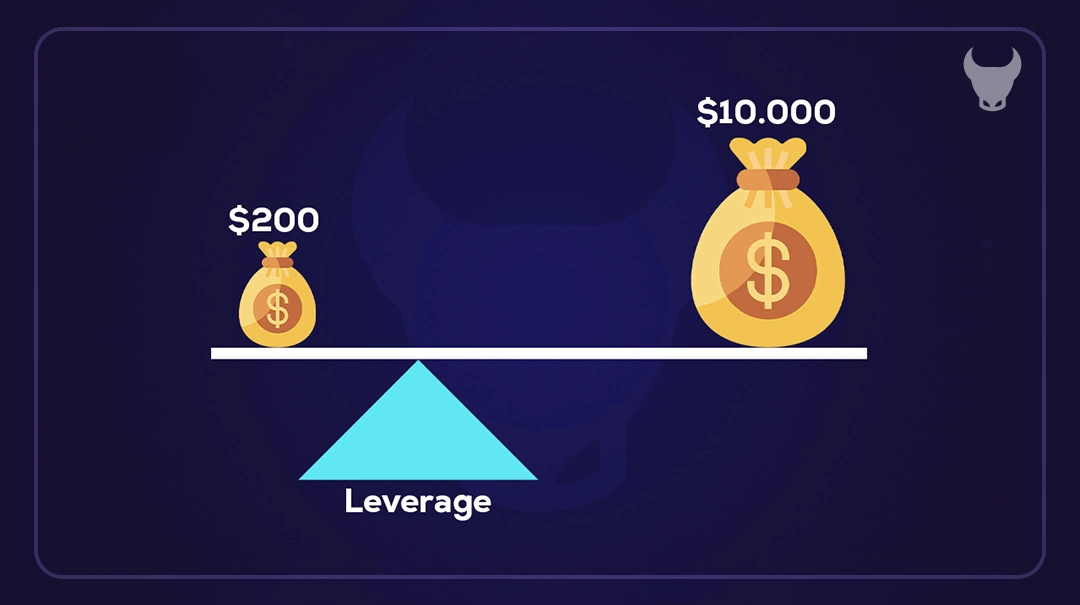
Relationship between Leverage and Margin
Leverage and margin are closely related concepts in forex trading. Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It acts as a security deposit to cover potential losses. The relationship between leverage and margin is inverse: the higher the leverage, the lower the margin requirement. For instance, if your broker offers a leverage of 1:50, the margin requirement would be 2% of the total trade value. Conversely, a leverage of 1:100 would require a margin of just 1%.
How Leverage Impacts Margin?
Leverage significantly impacts the margin required for trading. Higher leverage reduces the amount of margin needed to open a position, allowing traders to control larger positions with less capital. However, this also means that the risk of significant losses increases. For example, with high leverage, even a small adverse movement in the market can lead to substantial losses, potentially exceeding your initial investment. Therefore, while leverage can enhance trading opportunities, it also necessitates careful risk management to avoid margin calls and forced liquidation of positions.
What is Stop Out?
A stop out in forex trading is a critical mechanism that protects traders from incurring excessive losses. It occurs when a trader’s margin level falls to a specific percentage, known as the stop out level, at which point the broker automatically closes one or more of the trader’s open positions. This action is taken to prevent the account from falling into a negative balance.
When you trade on margin, your broker requires you to maintain a certain level of equity in your account to support your open positions. If the market moves against your trades and your equity drops below the required margin level, the broker will initiate a stop out. This means that the broker will start closing your most unprofitable positions first, until your margin level is back above the stop out threshold.
The stop out level varies between brokers but is typically set around 20% to 50% of the required margin. For example, if your broker has a stop out level of 20%, and your margin level falls to this point, your positions will be liquidated to prevent further losses.

What is Stop out Level?
A stop out level in forex trading is a predefined point at which your broker will automatically close one or more of your open positions. This happens when your margin level falls to a specific percentage, indicating that you no longer have sufficient equity to support your open trades.
The stop out level is set by your broker and varies between different brokers. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the required margin. For example, if your broker has a stop out level of 20%, it means that if your margin level drops to 20% of the required margin, the broker will start closing your positions to prevent further losses.
This mechanism is designed to protect both the trader and the broker. For the trader, it prevents the account from going into a negative balance, which could result in owing money to the broker. For the broker, it ensures that they can recover the funds lent to the trader for leveraged positions.
The Relationship between Stop Out & Margin
The relationship between stop out and margin is fundamental to understanding risk management in forex trading. Here’s a simple explanation:
Margin: When you open a leveraged position in forex trading, you are required to deposit a certain amount of money, known as margin. This margin acts as a security deposit to cover potential losses. The margin requirement is set by your broker and varies depending on the currency pair and market conditions.
Stop Out: A stop out occurs when your margin level falls to a specific percentage, known as the stop out level. This level is predefined by your broker and typically ranges from 20% to 50%. When your margin level reaches this point, your broker will automatically close one or more of your open positions to prevent further losses and protect your account from going into a negative balance.
How They Interact: The margin level is calculated as a percentage of your equity to the used margin. If the market moves against your position, your equity decreases, and so does your margin level. When the margin level drops to the stop out level, the broker intervenes to close positions. This automatic closure helps ensure that you do not lose more money than you have in your account.
Example: Suppose your broker has a stop out level of 20%. If your account equity falls to 20% of the required margin, the broker will start closing your positions. For instance, if you have $1,000 in your account and the required margin is $5,000, your margin level is 20%. If the market moves against you and your equity drops to $1,000, the broker will close your positions to prevent further losses.

Pros and Cons of Trading on Margin
Trading on margin can be a powerful tool for forex traders, but it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a balanced look at the pros and cons:
Pros
1. Increased Buying Power: Margin trading allows you to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This increased buying power can amplify your potential profits, enabling you to take advantage of market opportunities that would otherwise be out of reach.
2. Leveraged Profit Potential: By using leverage, you can potentially earn higher returns on your investments. Even small market movements can lead to significant gains, making margin trading an attractive option for those looking to maximize their profits.
3. Short-Selling Opportunities: Margin accounts allow you to short-sell, which means you can profit from declining markets. This flexibility can be particularly useful in volatile market conditions, providing more opportunities to make money.
4. Diversification: With margin trading, you can diversify your portfolio without needing a large amount of capital. This can help spread risk across different assets and reduce the impact of any single investment’s poor performance.
Cons
1. Increased Risk Exposure: While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses. If the market moves against your position, you can lose more money than you initially invested. This increased risk exposure requires careful management and a solid understanding of market dynamics.
2. Interest Payments: Borrowing funds to trade on margin comes with interest costs. These interest payments can add up over time, eating into your profits. It’s important to factor in these costs when calculating potential returns.
3. Margin Calls: If your account equity falls below the required margin level, you may receive a margin call from your broker. This requires you to deposit additional funds to maintain your positions. Failure to meet a margin call can result in the broker closing your positions, potentially at a loss.
4. Emotional Stress: The high stakes of margin trading can lead to significant emotional stress. The potential for large gains and losses can create pressure, making it difficult to stick to your trading plan and make rational decisions.
5. Market Volatility: Margin trading is particularly susceptible to market volatility. Sudden price swings can quickly erode your equity, leading to margin calls and forced liquidations. This makes it essential to have a robust risk management strategy in place.
In summary, trading on margin offers both significant opportunities and substantial risks. By understanding the pros and cons, you can make informed decisions and develop strategies to manage your risk effectively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Margin Trading
Margin trading can be highly rewarding, but it also comes with significant risks. To help you navigate this complex landscape, here are some common mistakes to avoid:
1. Overleveraging
One of the most frequent mistakes is overleveraging, which means borrowing too much money relative to your account size. While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. It’s crucial to use leverage wisely and not exceed a comfortable borrowing ratio. Overleveraging can quickly deplete your account if the market moves against you.
2. Lack of Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential in margin trading. Failing to set stop-loss orders or neglecting to monitor your positions can lead to substantial losses. Always establish clear risk parameters, set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and regularly review and adjust your positions based on market conditions.
3. Ignoring Margin Calls
A margin call occurs when your account equity falls below a certain threshold set by your broker. Ignoring margin calls can have severe consequences, including the forced liquidation of your positions. It’s important to promptly address margin calls by either depositing additional funds or closing out positions to meet the required margin level.
4. Chasing Unrealistic Returns
The allure of high returns can lead to impulsive trading decisions. Greed and the fear of missing out (FOMO) can cloud judgment. It’s important to set realistic profit targets, stick to your trading plan, and avoid making emotional trades based on short-term market fluctuations.
5. Insufficient Market Knowledge
Margin trading requires a deep understanding of the market and the assets being traded. Failing to conduct thorough research and analysis can lead to poor investment decisions. Stay informed about market trends, news, and fundamental factors that can impact the value of your positions. Developing a solid trading strategy based on sound analysis can greatly enhance your chances of success.
6. Neglecting to Diversify
Concentrating your margin trading positions in a single asset or market can expose you to unnecessary risk. Diversifying your portfolio helps spread risk across different assets and reduces the impact of any single investment’s poor performance.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can increase your chances of success in margin trading. Remember, effective risk management and a disciplined approach are key to navigating the complexities of margin trading.
Tips for Effective Margin Trading
Margin trading can be a powerful strategy, but it requires careful planning and risk management. Here are some essential tips to help you trade effectively on margin:
1. Understand the Terms and Rules
Before you start margin trading, make sure you fully understand the terms and rules set by your broker. This includes knowing the leverage limits, interest rates, and margin requirements. Familiarize yourself with the broker’s policies to avoid unexpected surprises.
2. Use Stop-Loss Orders
Implementing stop-loss orders on every trade is crucial. A stop-loss order automatically closes your position if the market moves against you by a certain amount, limiting your potential losses. This helps protect your capital and manage risk effectively.
3. Maintain a Margin Cushion
Always keep a buffer above the required margin level. This extra cushion can help you avoid margin calls and forced liquidations during market volatility. By maintaining a healthy margin level, you can trade with more confidence and stability.
4. Monitor Your Positions Regularly
Keep a close eye on your open positions and margin levels. Regular monitoring allows you to react quickly to market changes and adjust your trades accordingly. Use real-time quotes, news feeds, and technical analysis tools to stay informed.
5. Avoid Overleveraging
While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Avoid the temptation to overleverage your account. Start with lower leverage ratios and gradually increase them as you gain more experience and confidence.
6. Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification helps spread risk across different assets and reduces the impact of any single investment’s poor performance. By diversifying your portfolio, you can manage risk more effectively and improve your chances of long-term success.
7. Stay Informed
Stay updated with market news, trends, and economic indicators that can impact your trades. Continuous learning and staying informed about the forex market will help you make better trading decisions and adapt to changing market conditions.
8. Have a Trading Plan
Develop a clear trading plan that outlines your goals, risk tolerance, and strategies. Stick to your plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements. A well-defined plan helps you stay disciplined and focused.
9. Manage Your Emotions
Trading on margin can be stressful, especially during volatile market conditions. It’s important to manage your emotions and avoid making decisions based on fear or greed. Stay calm, stick to your plan, and make rational decisions.
By following these tips, you can enhance your margin trading strategy and manage risks more effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding margin in forex trading is essential for anyone looking to navigate this dynamic market effectively.
By grasping the concepts of leverage, margin requirements, and the various types of margins, traders can make informed decisions and manage their risks more efficiently. Margin trading offers significant opportunities for profit, but it also comes with substantial risks.
Therefore, it’s crucial to employ sound risk management strategies, avoid common mistakes, and stay informed about market conditions. By following the tips provided, you can enhance your trading strategy and increase your chances of success.