In the world of forex trading, the concept of ‘lot’ or ‘trading volume’ holds significant importance. It is a fundamental concept that traders need to grasp before embarking on their journey in the fascinating world of trading.
The reason behind its criticality lies in its role in risk assessment and capital management. Without a clear understanding the answer to “What is a lot in forex trading?” and “What is volume in forex?” questions, these crucial aspects of trading become unattainable. In this article, our educational team at Trendo will delve into this concept in detail and provide answer to an important “What is a lot in forex?” question. Stay tuned for an insightful discussion!
What Is the Forex Trading Volume and Lot?
Read this section carefully to understand the volume lots meaning in the forex market. In the forex market, the term ‘trading volume’ or ‘lot’ refers to the quantity of a currency pair or asset that is bought or sold. Traders determine the volume of their transactions in terms of ‘lots’. A single lot is equivalent to 100,000 units of the base currency. For example, buying 1 lot of the USDCHF currency pair means buying $100,000 against the franc currency.
When it comes to the relationship between leverage and lots, it’s important to note that an account with higher leverage allows for trading more lots. This is because higher leverage necessitates a smaller margin or credit for trading. Thus, the potential for trading increases with the leverage of an account.
Types of Forex Lot Sizes
Brokers typically offer four types of volumes or lot units to cater to a wide array of traders with varying capital. These are:
Standard Lot:
The standard lot size forex refers to a lot size of 100,000 units of the base currency. To illustrate, consider a trader who executes a transaction of 1 standard forex lot in the EURUSD currency pair at an exchange rate of 1.17. In this scenario, the trader, excluding leverage, would need to purchase 117,000 euros. Consequently, in this type of transaction, each pip movement in price equates to a value of $10.
The standard lot size forex is the best for experienced traders with large accounts ($50,000+), as losses can accumulate quickly for novices.
Mini Lot:
Mini lot refers to a lot size of 10,000 units of the base currency. For instance, if a trader executes a transaction of 1 mini lot in the EURUSD currency pair at an exchange rate of 1.17, the trader, excluding leverage, would need to purchase 11,700 euros. In such a transaction, the value of each pip of the price movement will be $1.
Trading based on mini lots is suitable for intermediate traders with moderate accounts ($5,000–$20,000) who have some experience and can handle slightly higher risk.
Micro Lot:
The micro lot size equals 1,000 units of the base currency. For example, if a trader executes a transaction of 1 micro lot in the EURUSD currency pair at an exchange rate of 1.17, the trader, excluding leverage, would need to purchase 1,170 euros. In this type of transaction, each pip movement in price corresponds to a value of $0.1, or 10 cents.
Micro lot-based trading is ideal for novice traders with small accounts ($500–$5,000) to practice real trading without depleting their balance.
Nano Lot:
The nano lot size equals 100 units of the base currency. For example, if a trader executes a transaction of 1 nano lot in the EURUSD currency pair at an exchange rate of 1.17, the trader, excluding leverage, would need to purchase 117 euros. In this type of transaction, each pip movement in price corresponds to a value of $0.01, or 1 cent.
It is excellent for absolute beginners testing strategies on tiny accounts, but limited broker support makes it less practical.
Read More: How to use Take Profit and Stop Loss in Forex trading.
The forex lot types with full details are shown for comparison in the table below:
To gain a practical understanding of the concept of lot size and experience it with absolute monetary values, a profit and loss table based on lot size for the EUR/USD currency pair is provided:
Profit and Loss Table for EUR/USD
|
Lot Size |
Units |
Pip Value (USD) |
50 Pips Gain |
100 Pips Gain |
50 Pips Loss |
100 Pips Loss |
|
Standard (1.00) |
100,000 |
$10.00 |
+$500 |
+$1,000 |
-$500 |
-$1,000 |
|
Mini (0.10) |
10,000 |
$1.00 |
+$50 |
+$100 |
-$50 |
-$100 |
|
Micro (0.01) |
1,000 |
$0.10 |
+$5 |
+$10 |
-$5 |
-$10 |
|
Nano (0.001) |
100 |
$0.01 |
+$0.50 |
+$1 |
-$0.50 |
-$1 |
Lot Size vs Position Size
In forex trading, novice traders often conflate lot size and position size, yet distinguishing these concepts is essential for effective risk management.
- Lot Size: This refers to the standardized trading volume selected on the platform, expressed in lots (e.g., 0.01, 0.1, or 1.00 lots). One standard lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency and serves as the primary unit for measuring trade volume.
- Position Size: This represents the actual monetary value of your trade. For instance, at an EUR/USD exchange rate of approximately 1.17, a 0.01 lot corresponds to 1,000 units with a notional value of roughly $1,170, while a whole lot equates to approximately $117,000. Position size indicates the overall scale of exposure in the market.
- Risk per Trade: The actual potential loss, calculated based on lot size, stop-loss distance in pips, and pip value (e.g., 1 lot size in forex with a 50-pip stop-loss risks approximately $500 in major pairs). Risk per trade should be limited to 1-2% of account equity, independent of lot or position size.
Properly managing lot size forex ensures controlled risk exposure. Traders must prioritize risk calculation over perceived trade size to maintain long-term account sustainability.
Relationship Between Lot Size, Leverage, and Margin
Understanding the interplay between lot size, leverage, and margin is crucial for managing risk effectively in forex trading.
What is Leverage?
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with less capital. For example, with 1:100 leverage, a $1,000 deposit controls a $100,000 position (equivalent to 1 lot forex).
How is Margin Utilized?
Margin represents the amount of account equity required by the broker to open and maintain a position. It acts as a security deposit. The required margin is calculated as follows:
Margin = (Lot Size × 100,000 × Current Price) / Leverage
Higher leverage reduces the margin needed for larger lot sizes, allowing traders to open bigger positions with less capital. However, this also increases potential risk exposure.
Why is a Large Lot Size with High Leverage Dangerous?
Combining large lot sizes with high leverage significantly amplifies exposure to market movements. A relatively small adverse price change, for instance, 50 pips against a one-lot position at 1:500 leverage, can trigger a margin call or account stop-out, potentially resulting in substantial or total loss of capital.
Novice traders are particularly vulnerable, as the allure of amplified profits often leads to overexposure. To mitigate this, adhere to moderate leverage (typically 1:30 to 1:100) and limit risk to 1-2% of account equity per trade.
How to Calculate Lot Size in Forex: A Step-by-Step Guideline
Calculating the correct lot size is one of the most essential habits for beginners, as it helps protect your account and prevent losses while you learn.
Use this straightforward risk-based approach, aiming to risk only 1-2% of your account per trade:
-
Determine your account balance: Check your current equity (for example, $3,000).
-
Choose your risk percentage: Decide how much you’re willing to lose on this trade (e.g., 1% of $3,000 = $30).
-
Set your stop-loss in pips: Based on your technical analysis, place a realistic stop-loss (e.g., 50 pips).
-
Know the pip value per standard lot: For most major pairs, it’s $10 per pip.
-
Apply the lot size formula:
Lot Size = Risk Amount / (Stop-Loss in Pips × Pip Value per Standard Lot)
Example: $30 risk / (50 pips × $10) = $30 / $500 = 0.06 lots.
Many beginners rely on free online lot-size calculators for quick checks, but learning this method gives you greater control. Always round down slightly for extra safety and adjust as your account changes.
The lowest and highest amount of lots in brokers
The size of the lot for trading can vary depending on your broker. Most brokers, including Trendo International Broker, offer standard lots, mini lots, and micro lots for traders.
At Trendo Broker, the trading volume for each position ranges from a minimum of 0.01 lots to a maximum of 50 lots. This flexibility allows traders with any account balance to execute and manage their trades in the forex market effectively. As a result, traders with any amount of balance can execute and manage their trades in the forex market.
Choosing the right volume for trading
Capital management is a crucial principle in financial market trading. Given that each trader may have a unique capital management strategy and that trading volume is intrinsically linked to capital management, it’s essential to exercise caution when selecting a broker and the types of accounts they offer.
For instance, let’s consider trading in a real account with Trendo Broker. All accounts provided by Trendo Broker are of the ECN type.
To learn more about this account, you can refer to the following link: Trendo Broker Trading conditions and rules
Remember, the right knowledge and careful planning are key to successful trading.
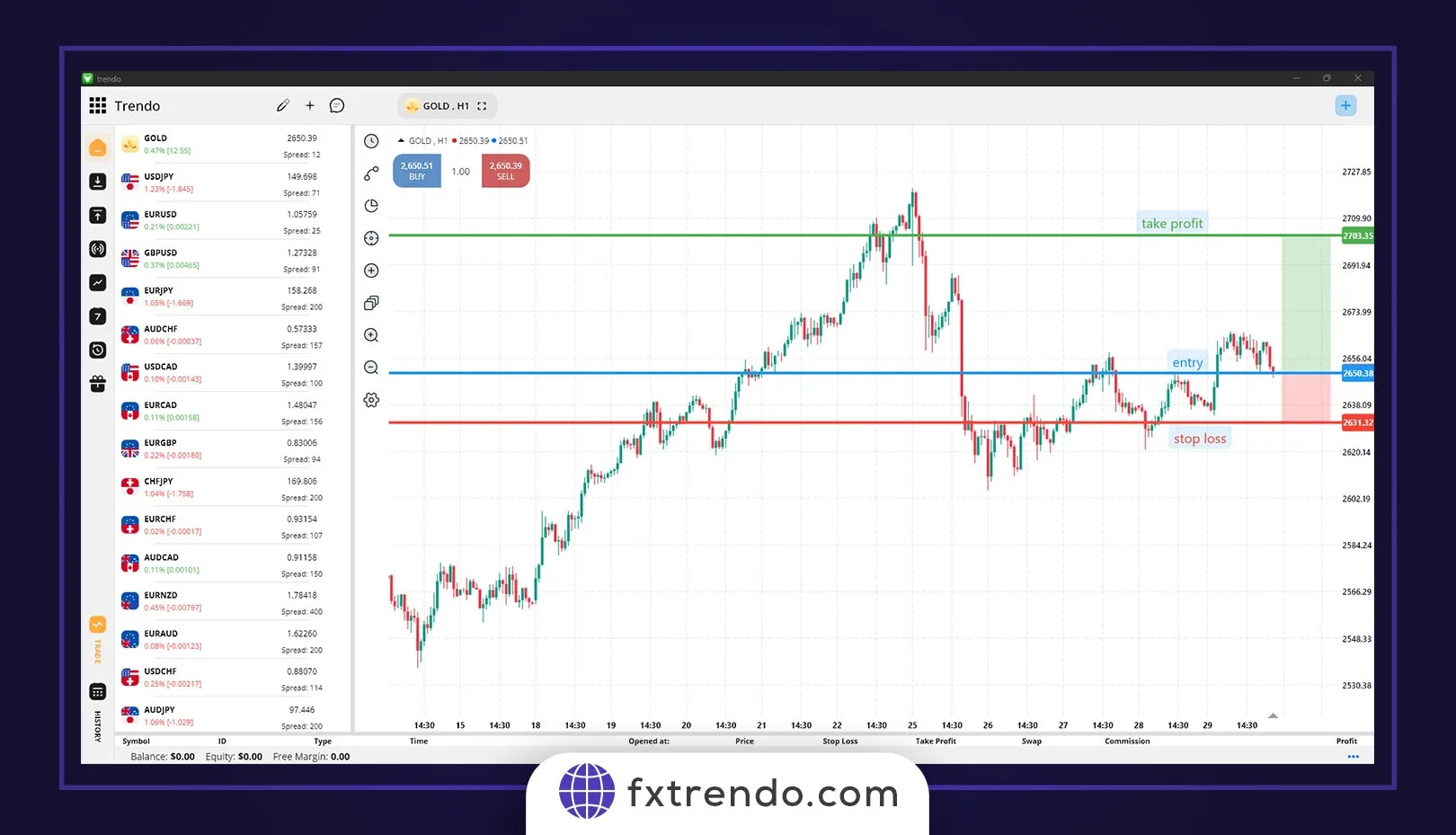
As a professional trader, you must calculate your potential profit or loss before entering a trade and be fully prepared for both situations. We recommend never risking more than 2% of your total capital on a single trade. Suppose an account balance is $1000. So, we can only risk $20 per trade. If the stop-loss is triggered in this transaction, we should lose no more than $20. Considering the value of $20, we go to the price chart.
For example, according to the picture below, we intend to enter into a transaction to buy gold at the 2144 price and set the stop loss at 2139.
Since our stop loss in this transaction is 50 pips, we calculate our trading volume via the following formula:
In this example, with a risk amount of $20 and a stop loss of 50 pips, our trading volume will be 0.04 lots. You can also easily use Trendo’s Forex calculator to calculate your profit in a trade. Also, in case you want to know the concept of pip and how to calculate the profit and loss of your transactions, we recommend referring to the following article:
Read More: What is Pip in Forex?
Common Mistakes Traders Make With Lot Size
Amateur traders often struggle with lot sizing, resulting in avoidable losses. Recognizing these common errors can help you trade more safely and consistently.
Overleveraging
Many beginners use maximum leverage to open large lots, hoping for fast profits. However, even a small market move against you can trigger a margin call, wiping out your account quickly. Stick to moderate leverage and small lots until you gain experience.
Using a Fixed Lot Size
A frequent mistake is trading the same lot size forex (e.g., always 0.1 lots) regardless of your current account balance or market volatility. As your account grows or shrinks, this can turn a safe risk into a dangerous one, potentially exposing you to far more than your planned 1-2%.
Ignoring Stop-Loss Distance
Traders set wide stop-losses but keep the same lot size forex. For example, a 100-pip stop with your usual lot might risk $100 instead of your target $20. Always adjust lot size downward for larger stops to keep risk consistent.
Revenge Trading with Larger Lots
After a loss, some traders increase the lot size to “win it back” quickly. This emotional decision often leads to even bigger losses and account blow-ups.
To avoid these pitfalls, always calculate lot size based on your current balance, risk tolerance (1-2%), and stop-loss distance before every trade. Discipline protects your capital.
Summary
In this article, we’ve explored the concept of ‘Lot’ and ‘trading volume’, and demonstrated how to calculate transaction volumes using a real account example from Trendo Broker. As a professional trader, it’s essential to apply this formula in every trade you make and maintain constant control over your risk in each transaction.
We recommend risking a maximum of 2% in one transaction and a maximum of 5% of your total capital on each trading day. This approach will help you manage your capital effectively and mitigate potential losses.